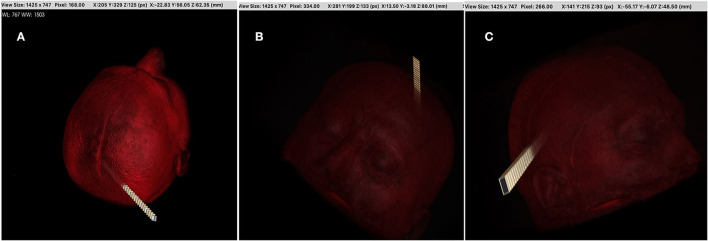
Figure 4.
The research algorithm was created for time efficiency compared with the time-consuming RL algorithm. The goal is to find the most ideal cranial entry points. Machine learning was not used in this method. Cranial entry points were scored using the equivalent areas and tumor location in Table 1 and compared with each other. With this algorithm, it was possible to sort by five most ideal entry points, 10 entry points, or worst entry points. In addition, this algorithm provided a linear access path to tumor tissue in the shape of a rectangular prism or cylinder. The entrance area in the images was determined as 1.5 cm2. The algorithm has been adjusted to allow this area to be increased or decreased. This algorithm can be useful in tubular operative systems or rigid endoscopic systems. In this study, we took these points (the most ideal 4,900 points) as the starting points of RL. Image (A,B) are the ideal best rated and image (C) the worst-rated sample entry points.