FIGURE 2.
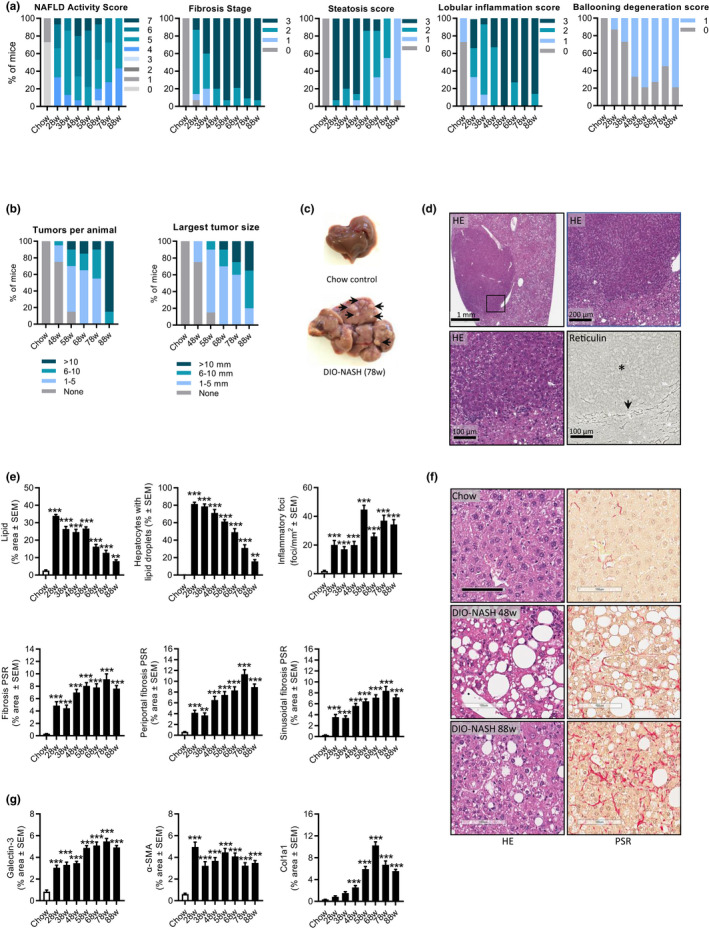
GAN DIO‐NASH mice show progressive development of severe fibrosing NASH and hepatocellular carcinoma. Mice were fed the GAN diet for 28–88 weeks (n = 11–15 per group). (a) NAFLD Activity Score (NAS), fibrosis stage, steatosis score, lobular inflammation score, and ballooning degeneration score. (b) Total number of hepatic tumors and largest liver tumor size (diameter, mm) per animal. (c) Representative whole‐liver of chow‐fed control and GAN DIO‐NASH mouse (78 weeks of feeding), respectively. The latter showing multiple tumors (arrows). (d) Cytologic and architectural characteristics of liver neoplastic lesions in DIO‐NASH mice (≥58 weeks of GAN diet feeding). The tumor demonstrates increased hepatocyte nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio (condensed cytoplasm with normal or enlarged nuclei) and absent reticulin trabecular framework (asterisk), a morphological characteristic of HCC. The compression zone between neoplastic and normal liver parenchyma is indicated by an arrow. Representative photomicrophraphs of HE‐ and reticulin‐stained tumor sections. Insert in upper left panel (HE staining) is further magnified in upper right and lower left panel. (e) GHOST‐based histomorphometrics. Proportionate (%) area of lipids; hepatocytes with lipid droplets relative to total hepatocyte counts; number of inflammatory foci per mm2; percentage total sectional area of fibrosis¸ percentage area of periportal fibrosis; and percentage area of perisinusoidal fibrosis (picro‐Sirius Red [PSR]). (f) Representative photomicrographs of HE and PSR stainings illustrating the development of steatosis and perisinusoidal fibrosis in DIO‐NASH mice (scale bar, 100 µm). (g) Conventional histomorphometrics. Percentage area of galectin‐3; α‐SMA, and Col1a1. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (Dunnett’s test one‐factor linear model). There was a minor loss of mice related to increased aging and the extended high‐fat diet feeding periods applied. DIO, diet‐induced obese; GAN, Gubra‐Amylin non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) diet; GHOST, Gubra Histopathological Objective Scoring Technology; HE, hematoxylin‐eosin; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; PSR, picro‐Sirius Red.
