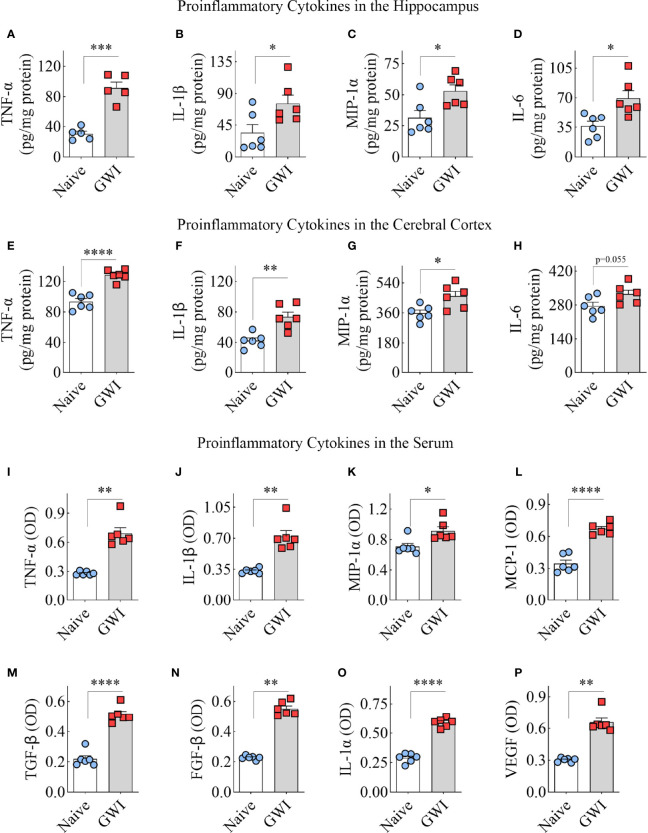
Figure 6.
Animals with chronic Gulf War Illness (GWI) displayed an increased concentration of proinflammatory cytokines in the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and circulating blood. The bar charts A–H compare tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α; A, E), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β; B, F), macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1α; C, G), and interleukin 6 (IL-6; D, H) concentrations in the hippocampus (A–D) and the cerebral cortex (E–H) between naïve and GWI rats. The bar charts (I–P) compare TNF-α (I), IL-1β (J), MIP-1α (K), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1; L), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β; M), fibroblast growth factor-beta (FGF-β; N), interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α; O), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF; P) concentrations in the serum between naïve and GWI rats. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001.