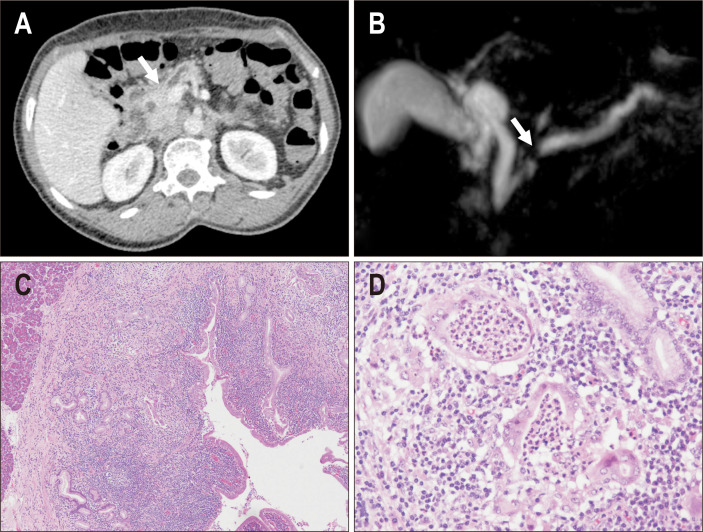
Fig. 4.
A case of type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) that presented with pancreatic duct obstruction. (A) Computed tomography showed duct obstruction in the pancreatic head (arrow); however, a mass lesion was not confirmed. (B) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showing obstruction of the main duct at the pancreatic head (arrow) and dilatation of the upstream duct. (C) In the resected specimen, a dense inflammatory infiltrate was observed along the duct system, and pancreatic parenchyma was not inflamed (left upper area) (H&E, ×20). (D) A granulocytic epithelial lesion was confirmed in the damaged pancreatic duct (H&E, ×100).