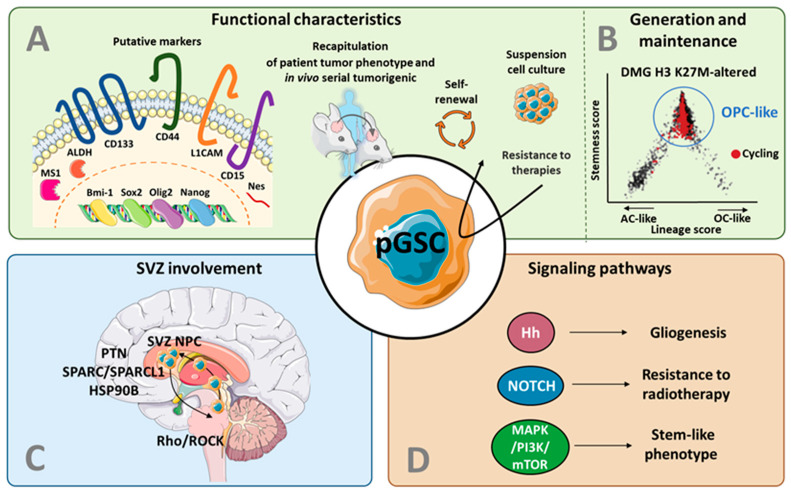
Figure 2.
Graphical summary illustrating the functional evidences of GSCs existence in pHGG (A), their generation and maintenance in pHGG (B), the role of the SVZ (C), and the signaling pathways involved in GSC-features (D). While there is no clear consensus, glioma stem cells (GSC) are classically defined based on multiple functional criteria, including the expression of different levels and patterns of surface and intracellular markers, the formation of spherical colonies in suspension cultures, a higher resistance to radiation and/or chemotherapy compared to the non-GSCs tumoral cells and the potential to recapitulate the initial tumor heterogeneity (A). scRNA-seq analysis of primary Diffuse Midline Glioma (DMG) H3 K27-altered showed that tumor cells are mostly constituted of cells that resemble oligodendrocyte precursor cells, which display an enhanced proliferative and tumor-propagating capacity compared to the minority of more differentiated cells (astrocyte-like and oligodendrocyte-like) (B). The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a key actor in pediatric high-grade gliomas (pHGG), as suggested by the recent in vivo demonstration that DMG cells injected in the pons migrate towards the SVZ in response to chemoattractant signals secreted by SVZ-hosted neural precursor cell. This chemoattractant effect depends on the pleiotrophin (PTN) and its three binding partners and is mediated by the PTN receptor protein tyrosine phosphate receptor type Z and the activation of the Rho/Rho kinase pathway (C). Several signaling pathways are shared between neural stem cells and pediatric GSC and are involved in gliogenesis, resistance to radiotherapy, and stem-like phenotype of pHGG (D). Abbreviations: AC: astrocyte; ALDH: aldehyde dehydrogenase; Bmi-1: B cell-specific moloney murine leukemia virus integration site 1; DMG: diffuse midline glioma; Hh: hedgehog; HSP90B: heat shock protein 90B; L1CAM: L1 cell adhesion molecule; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MSI1: mushashi-1; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; Nes: nestin; NPC: neural precursor cell; OC: oligodendrocyte; Olig2: oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2; OPC: oligodendrocyte progenitor cell; pGSC: pediatric glioma stem cell; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3′–kinase; PTN: pleiotrophin; ROCK: Rho-associated protein kinase; Sox2: SRY-Box transcription factor 2; SPARC: secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine; SPARCL1: SPARC-like protein 1; SVZ: subventricular zone. The schematic art pieces used in this figure were provided by Servier Medical art (https://smart.servier.com), 25 April 2022. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Figure 2B is adapted from Filbin et al. [56].