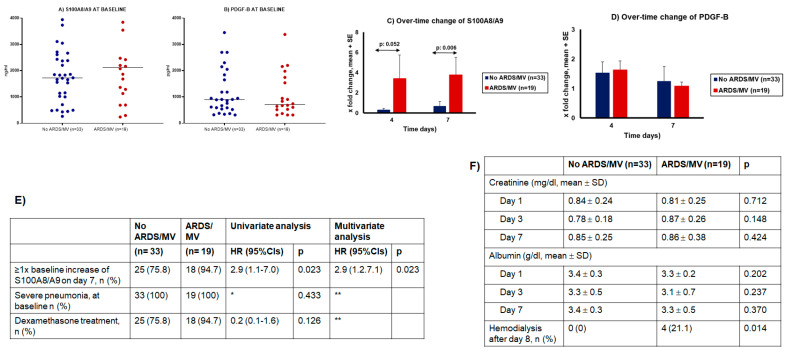
Figure 7.
S100A8/A9 (calprotectin) as an independent variable of progression into acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) necessitating mechanical ventilation (MV). The analysis involved serial measurement among 52 patients with severe COVID-19 participating in the SAVE-MORE study. (A) Circulating concentrations of calprotectin at baseline. No significant differences were found between patients who progressed into ARDS in need of MV and those who did not progress into ARDS in need of MV. (B) Circulating concentrations of PDGF-B at baseline. No significant differences were found between patients who progressed into ARDS in need of MV and those who did not progress into ARDS in need of MV. (C) Changes of circulating concentrations of calprotectin on days 4 and 7 of follow-up from baseline. The p values of comparisons are provided. (D) Changes of circulating concentrations of PDGF-B on days 4 and 7 of follow-up from baseline. No significant differences were found between patients who progressed into ARDS in need of MV and those who did not progress into ARDS in need of MV. (E) Univariate and multivariate forward stepwise Cox regression analysis of variables associated with progression into ARDS and MV; * HR cannot be calculated because one value is zero; ** excluded after two steps of forward analysis. (F) Serum concentrations of creatinine and albumin. The p values of comparisons are provided. Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; PDGF = platelet-derived growth factor.