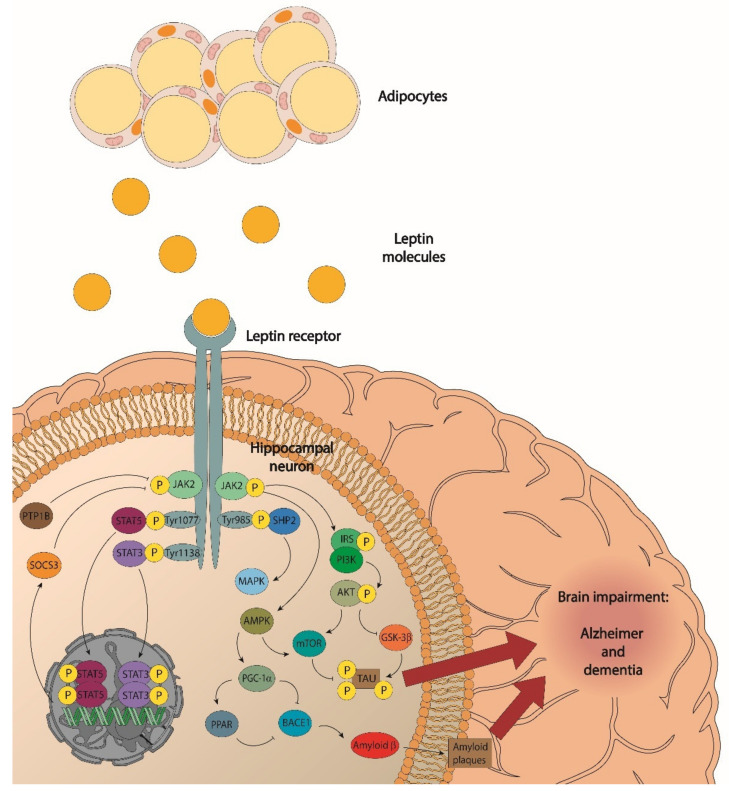
Figure 1.
Leptin signalling in a hippocampal neuron. Leptin, mainly released by adipose tissue, reaches a hippocampal neuron where, binding to LepRb, activates the JAK/STAT, PI3K/Akt, and AMPK signalling pathways. PI3K/Akt pathway activation leads to mTOR activation, influencing synthesis and aggregation of Tau, as well as GSK-3β inactivation, which, in turn, is not able to hyperphosphorylate Tau. AMPK pathway activation leads to PGC-1α and PPAR activation, which, translocated to the nucleus, inhibit BACE1 transcription and decrease Aβ production. SOCS3 and PTP1B are negative regulators of leptin signalling acting on JAK2 and, therefore, generate leptin resistance that may cause the worsening of AD.