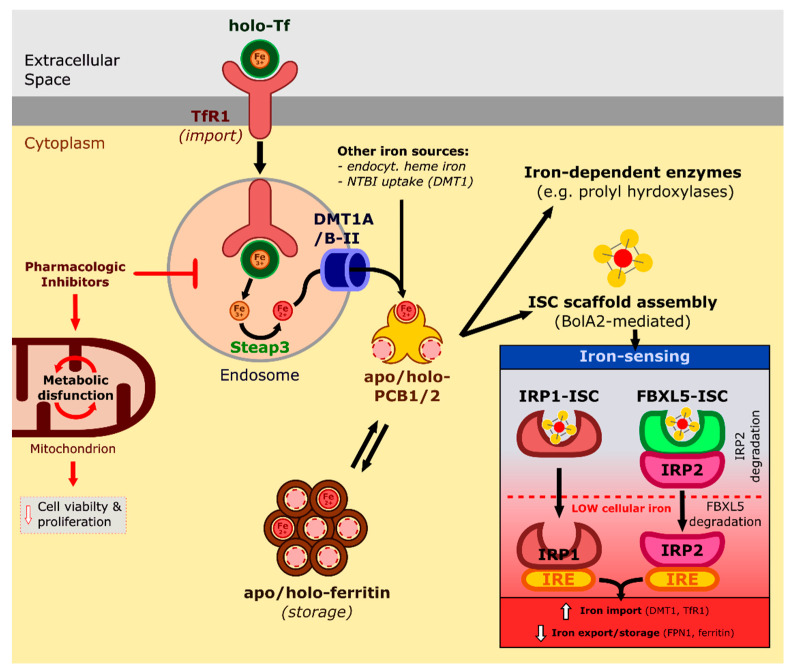
Figure 1.
Transport and regulation of intracellular iron levels. Transferrin (Tf)-bound iron is internalised through the transferrin receptor (TfR1) pathway. Inside the endosome, imported ferric iron is released and reduced to ferrous iron by Steap3. DMT1A/B-II transports ferrous iron to the cytoplasm, where it binds to PCB1/2. Cytoplasmic iron can either be stored in ferritin or incorporated into iron-dependent enzymes or the assembly of iron–sulfur cluster (ISC) scaffolds. Low levels of intracellular iron can hinder ISC assembly, thus activating the IRP1/2 iron-sensing pathways as the activity of both IRP1 and FBXL5-IRP2 is dependent on ISC availability. Activated IRP1/2 can bind to iron response elements (IREs) which regulate iron import, export and storage.