Table 4.
PSMA-i labeled with [99mTc][Tc(CO)3]+-fragment in a multivalent approach.
| Chelator/Linker/Scaffold | Affinity | Performance | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
[Tc(CO)3]15–16
(2020) |
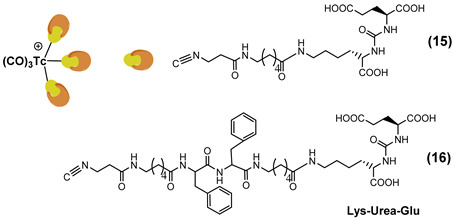
|
a 5.50 ± 0.99 (15) 0.20 ± 0.01 (16) |
Complexes were investigated on 22Rv1 xenografts. Moderate PSMA-dependent tumor uptake 1.87 ± 0.11% ID/g, at 1 h p.i, which increased to 2.83 ± 0.26% ID/g at 4 h. Clinical translation: No |
[118] |
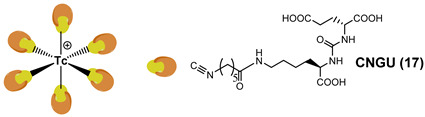
|
b 8.79 (17) | Complexes were investigated on LNCaP xenografts. PSMA mediated tumor uptake: 4.86 ± 1.19% ID/g at 1 h p.i. High kidneys 70.95 ± 12.28% ID/g and spleen 5.84 ± 1.51% ID/g uptakes. Tumor-to-blood ratio was 2.89 and tumor–to–muscle ratio was 12.46. Liver and intestinal uptake were 2.46 ± 0.72 and 2.16 ± 0.34% ID/g, respectively. Clinical translation: No |
[119] |
a PSMA inhibitory affinity was determined using the corresponding technetium-99m complexes. Data are reported as KD (nM). 22Rv1 are PSMA-positive human prostate carcinoma epithelial cells, which have moderate PSMA expression [19,120]. b The binding affinity to PSMA of the unlabeled CNGU ligand was performed by using NAALADase assay on LNCaP cell lysates. Data are reported as the enzyme inhibitory constant (Ki nM).
