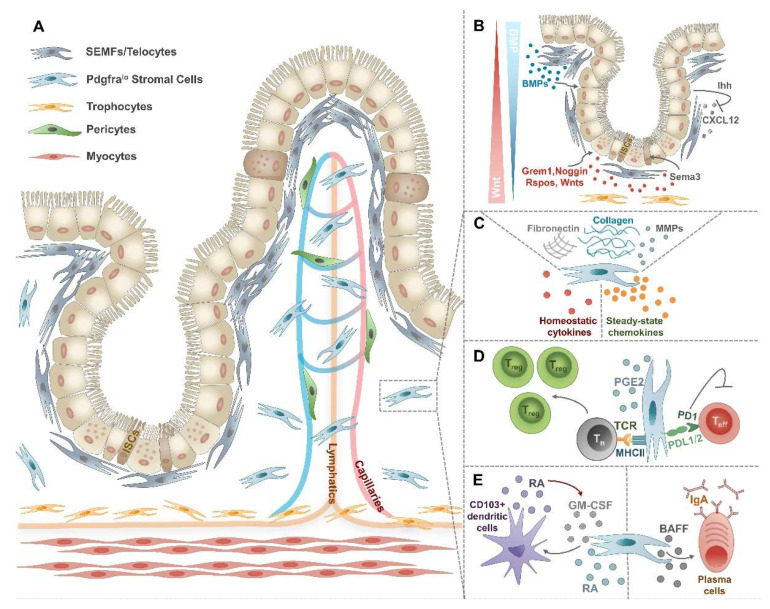
Figure 1.
Heterogeneity and functions of steady-state IMCs. (A) In the lamina propria and the muscularis mucosae distinct subsets of IMCs can be found. Directly underneath the epithelium, SEMFs or telocytes form an envelope. Pdgfralo stromal cells are dispersed along the crypt–villus length. Close to the muscularis externa and below the crypts, trophocytes form a stripe. Pericytes are found in the perivascular area. (B) SEMFs and trophocytes play a critical role in creating a niche for ISCs by the secretion of Wnt and BMPs. (C) Under steady-state conditions, IMCs not only excel in producing ECM components and matrix remodeling enzymes but also secrete a wide array of immunomodulatory cytokines and chemokines. (D) By the expression of PDL1/2 and MHC-II molecules, IMCs play a critical role in the maintenance of intestinal tolerance. (E) IMCs may induce tolerogenic CD103+ dendritic cells and IgA+ plasma cells, both of which contribute to intestinal homeostasis.