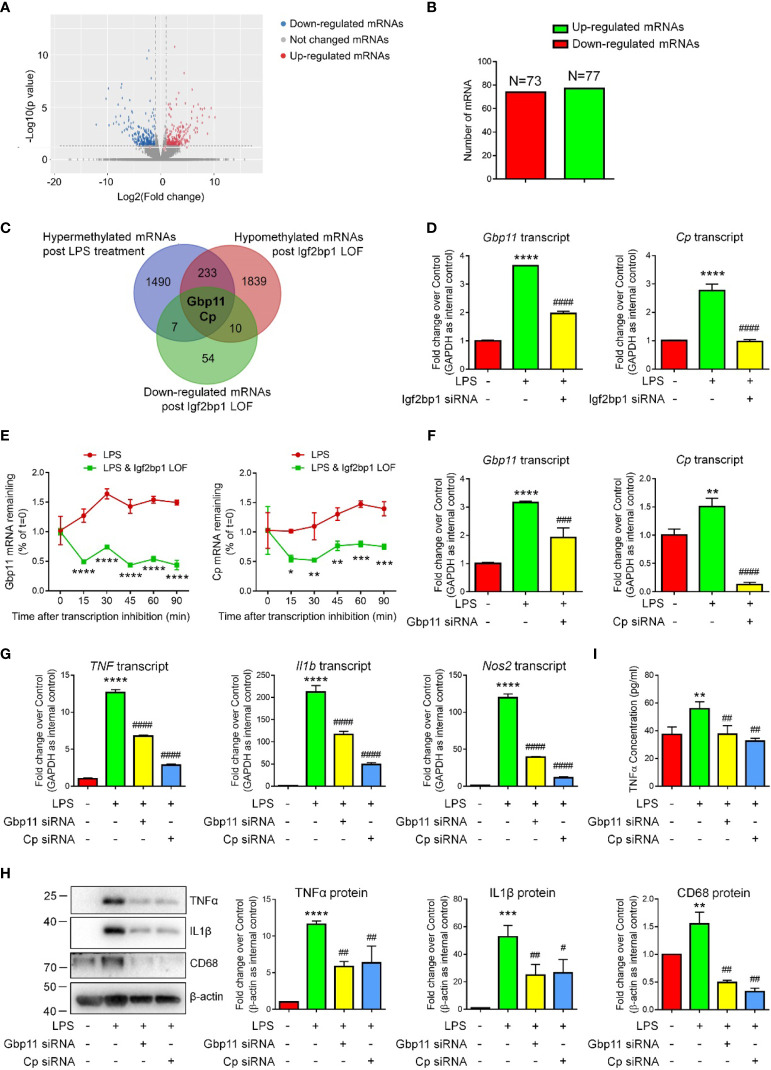
Figure 4.
Igf2bp1 regulates the inflammatory responses of microglia via stabilizing Gbp11 and Cp mRNAs. (A) Volcano plots showing the differentially expressed genes after knocking down Igf2bp1 expression in LPS-stimulated microglia. (B) The numbers of differentially expressed genes. (C) Venn diagrams for genes with m6A hypermethylation after LPS treatment, m6A hypomethylation post Igf2bp1 LOF, and reduced expression post Igf2bp1 LOF. (D) Expression of Gbp11 and Cp mRNAs in LPS-stimulated microglia after knocking down Igf2bp1 expression was determined by qRT-PCR. (E) Gbp11 and Cp mRNAs degradation in microglia treated with actinomycin D for the indicated times. (F) The knockdown efficiency of both Gbp11 and Cp siRNA in LPS-stimulated microglia was determined by qRT-PCR. (G) Expression of TNF, Il1b, and Nos2 mRNAs after knocking down either Gbp11 or Cp expression in LPS-stimulated microglia was determined by qRT-PCR. (H) Expression of TNFα, IL1β, and CD68 proteins after knocking down either Gbp11 or Cp expression in LPS-stimulated microglia was determined by western blotting. (I) The release of TNFα after knocking down either Gbp11 or Cp expression from LPS-stimulated microglia was determined by ELISA assay. Data were represented as mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments.*, **, ***, and **** denote p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001, and p < 0.0001, respectively, in comparison with control microglia. #, ##, ###, and #### denote p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001, and p < 0.0001, respectively, in comparison with LPS-stimulated microglia.