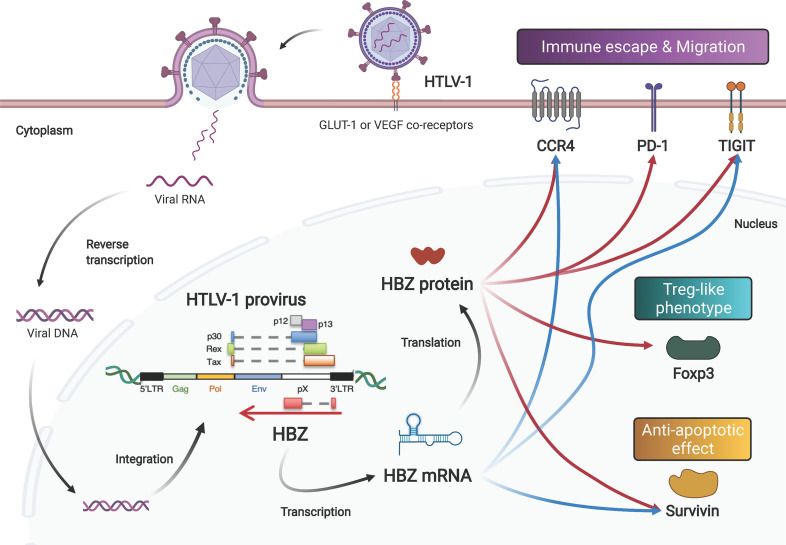
Figure 1.
Both the mRNA and protein products of the HTLV-1 HBZ gene function to induce proliferation, survival, and phenotype change of infected cells. After infection via its receptors (GLUT-1, neuropilin-1 and heparan sulfate proteoglycan), the HTLV-1 genome is integrated into the host’s DNA. HTLV-1 encodes viral genes in the sense and antisense strand of the provirus. The antisense gene, HBZ, is transcribed into mRNA, and subsequently translated into protein. Both the mRNA and the protein enhance the expression levels of CCR4, Tigit and Survivin. In addition, HBZ protein enhances transcription of PD-1 and Foxp3 genes.