Figure 2. Effects and molecular mechanisms of SCFAs on cell types and biological processes involved in bone fracture healing.
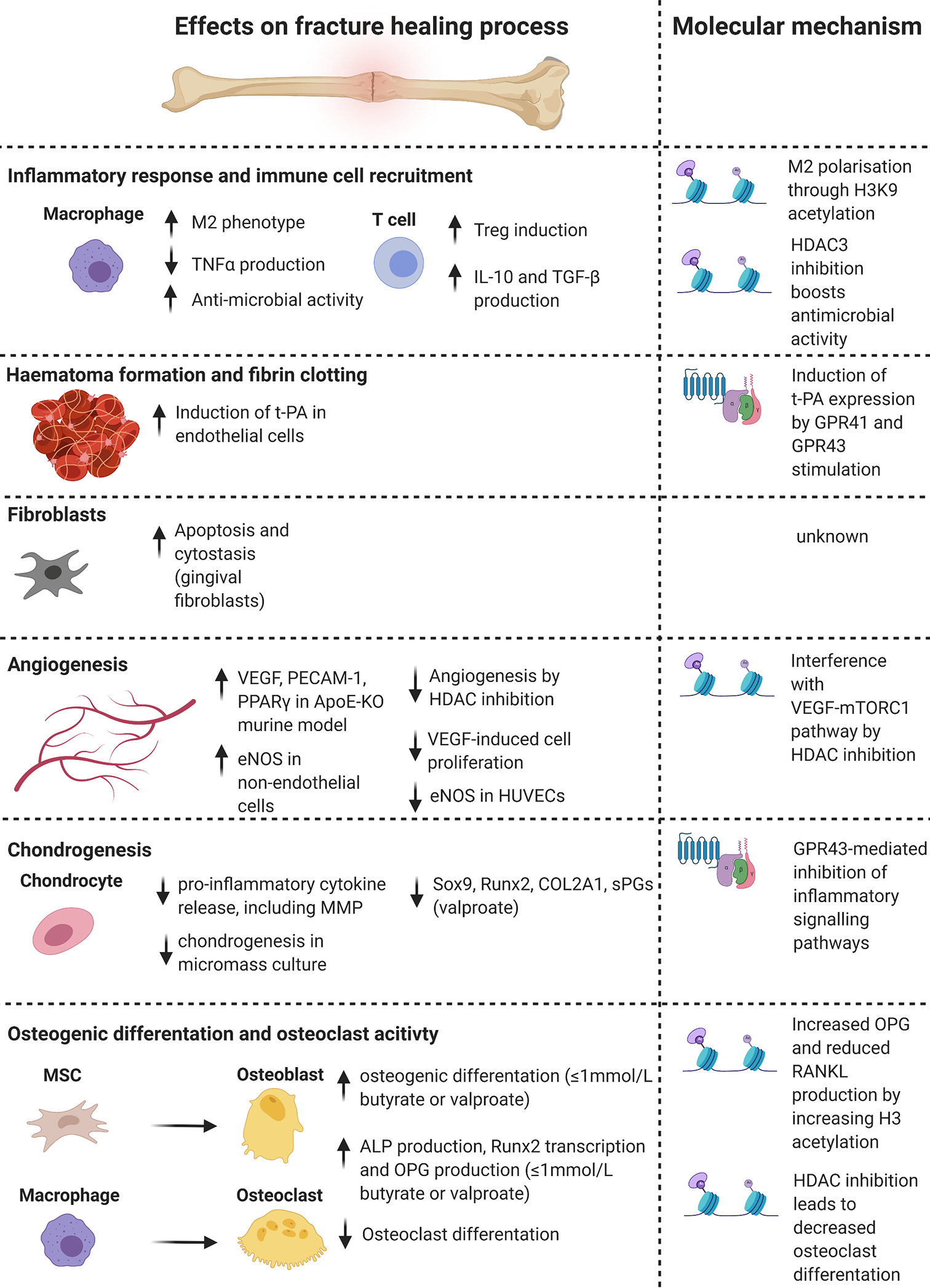
SCFAs influence the individual stages of fracture healing and the different cell types involved. Histone modifications, mainly mediated by HDAC inhibition, and GPR-signalling are the main molecular mechanisms mediating the effects of SCFAs. Abbreviations: SCFAs = Short-chain fatty acids, HDAC = Histone deacetylase, GPR = G protein-coupled receptor, M2= macrophage-phenotype 2, TNFα = Tumour necrosis factor α, IL-10 = Interleukin 10, TGF-β = Transforming growth factor β, H3K9 = Histone 3 Lysine 9, t-PA = tissue plasminogen activator, VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor, PECAM1 = platelet and endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1, PPARγ = Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, ApoE-KO = Apolipoprotein E knock-out, eNOS = endothelial nitric oxide synthase, HUVECs = human umbilical vein endothelial cells, mTORC1 = mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1, MMP = matrix metalloproteinase, Sox9 = sex determining region Y box 9, Runx2 = Runt-related transcription factor 2, COL2A1 = collagen type 2 alpha 1 chain, sPG = sulphated proteoglycan, MSC = mesenchymal stromal cell, ALP = alkaline phosphatase, OPG = osteoprotegerin, RANKL = receptor activator of NF-κB ligand. Figure created with BioRender.com.
