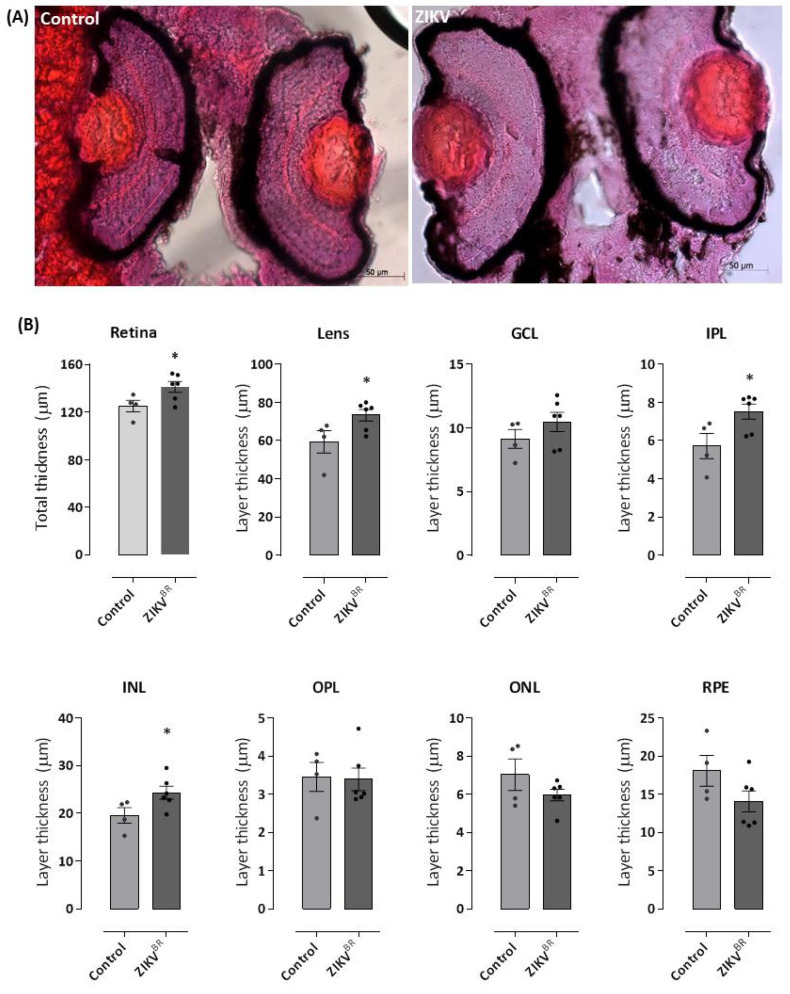
Figure 3.
ZIKV causes an increase in the thickness of the zebrafish retina, especially in the lens and inner nuclear layer. The 96 hpf larvae infected with ZIKVBR at 0 hpf or control group were fixed, dehydrated and rehydrated, incubated in 30% sucrose, and were mounted in OCT. Then, 18 μm-thick cryosections were stained with H&E. The images obtained under an optical microscope show an increased retinal layer thickness in ZIKV-infected larvae (A,B), which is most evident in the lens region. Red dots in the eyes of the control animals do not represent any morphological changes or developmental malformations. All measures were made in ImageJ software. GCL = ganglion cell layer; INL = inner nuclear layer; ONL = outer nuclear layer; IPL = inner plexiform layer; OPL = outer plexiform layer; RPE = retinal pigment epithelium. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05 compared with the negative control group.