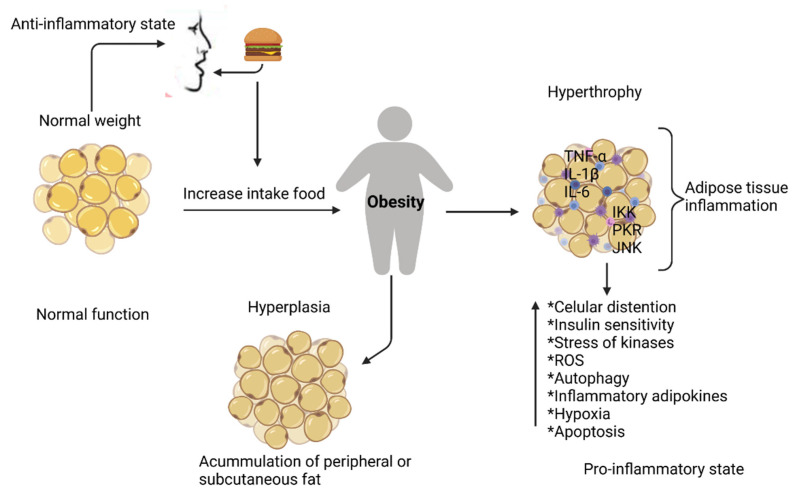
Figure 1.
Adipose tissue inflammation. Excessive growth of adipose tissue in obesity induces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that activate protein kinase pathways, at the same time stimulating macrophage infiltration and a change in the phenotype of M2-type macrophages to proinflammatory M1, leading to an inflammatory state with consequences locally and systemically. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1b (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), N-terminal c-JUN (JNK), nuclear factor-kappa kinase inhibitor β (IKK), protein kinase R (PKR). Created with BioRender.com.