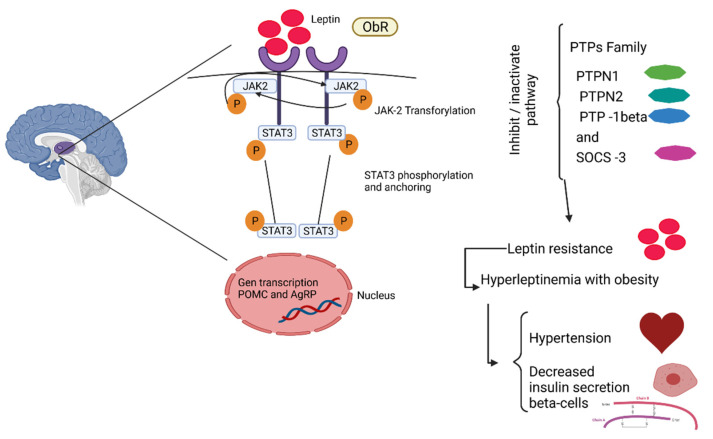
Figure 2.
Leptin pathway. Leptin binds to the ObR receptor and JAk-2 transphosphorylation occurs, translocating the phosphate groups, giving rise to the anchoring and phosphorylation of STAT3. These STA3 travel to the nucleus, where the transcription of target genes, such as POMC (decreases hyperphagia) and AgRP (increases food intake), takes place. This pathway can be inactivated by the interaction of tyrosine-protein phosphatase 3 (PTP3) and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3), causing resistance to leptin, resulting in hyperleptinemia, which leads to cardiovascular problems, such as hypertension, as well as causing a decrease in insulin secretion in β cells. Created with BioRender.com.