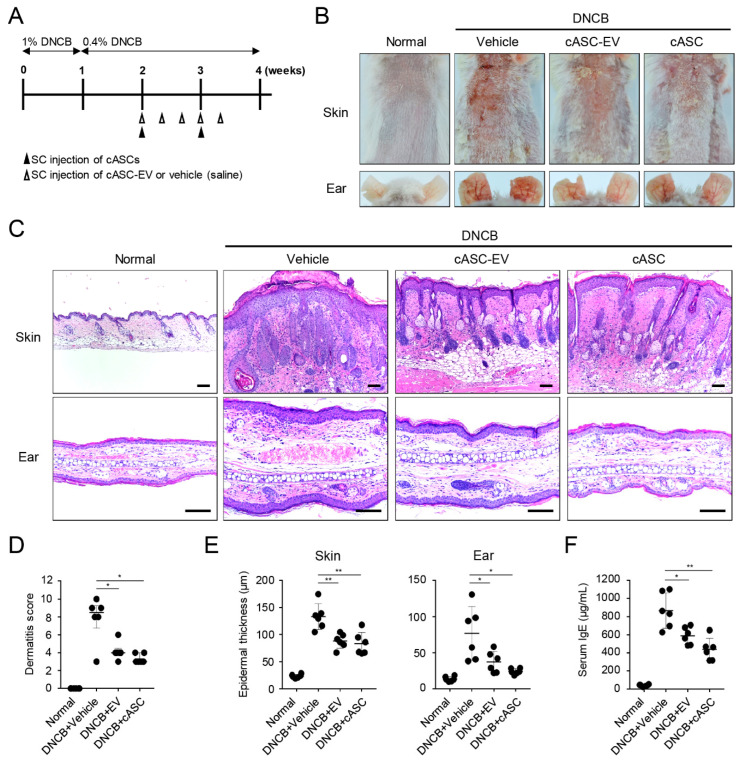
Figure 2.
cASC and cASC-EV improve DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion in Balb/c mice. (A) Schematic diagram for development of atopic dermatitis model by topical application of DNCB in Balb/c mice. After mice were sensitized with DNCB for 7 days, DNCB was further topically applied to the shaved dorsal skin and ear for 3 weeks. cASC was applied twice and cASC-EV was applied 5 times for 2 weeks (n = 6/group). (B) Representative dorsal skin and ear photographs of each treatment group showing comparison of AD-like skin lesions. (C) Tissue sections from the back skin and ear stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) The severity of dermatitis evaluated by a 3-point scoring index of atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis score was graded as 0 (absent), 1 (mild), 2 (moderate), or 3 (severe) based on the sum of the scores of clinical signs such as excoriation/erosion, scaling/dryness, edema, and erythema/hemorrhage. (E) Epidermal thickness of back skin and ear (n = 6/group). (F) The concentration of the serum total IgE levels measured by an ELISA. Dermatitis score represent median [IQR] (min–max) and the others represent mean ± SD. Significant value was * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. DNCB + Vehicle.