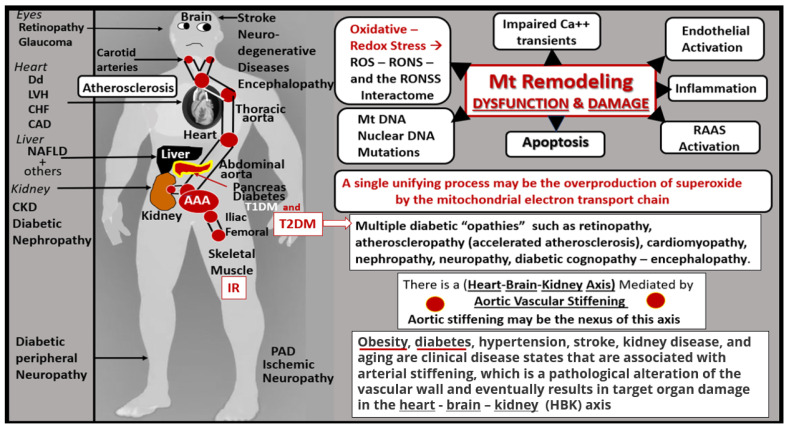
Figure 3.
Mitochondria (Mt) remodeling to an aberrant Mt (aMt) phenotype with dysfunction and damage to organ systems. This figure is an illustration of proposed mitochondrial-mediated mechanisms of disease development and progression associated with aMt dysfunction and damage that have been implicated in numerous organ systems and clinical diseases (left-hand standing man image). Oxidative—redox stress includes the sum of reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and reactive sulfur species (RSS) to create the reactive oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur species (RONSS) interactome. Importantly, aortic stiffening may be the nexus for a heart-brain-kidney axis (red circles) illustrating the aortic vascular pathway of vascular stiffening to affect the carotid and renal arteries and target organs of the heart-brain-kidney axis. AAA = abdominal aortic aneurysm; Ca++ = calcium transients; CAD = coronary artery disease; CHF = congestive heart failure; CKD = chronic kidney disease; Dd = diastolic dysfunction; DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid; IR = insulin resistance; LVH = left ventricular hypertrophy; NAFLD = non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; PAD = peripheral arterial disease; RAAS = renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; T1DM = type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM = type 2 diabetes mellitus.