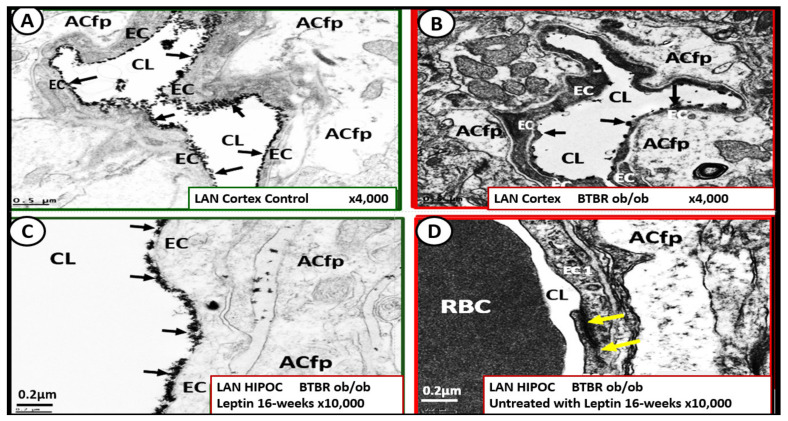
Figure 18.
Leptin replacement in the obese diabetic BTBR ob/ob protects the brain endothelial cell glycocalyx (ecGCx) in cortical layer III and hippocampus. Panel A demonstrates the continuous decoration of the ecGCx with lanthanum nitrate (LAN) staining in the heterozygous non-diabetic control model cortical layer III (arrows). Panel B depicts the marked attenuation and/or loss of the ecGCx in the obese diabetic BTBR ob/ob model cortical layer III and note when the ecGCx was present it was clumped and discontinuous (arrows). Panel C also demonstrates the continuous decoration of the ecGCx in hippocampus CA-1 regions of the BTBR ob/ob models that were treated with intraperitoneal leptin for 16-weeks and stained with LAN (arrows) and the ecGCx is comparable to the control model in panel A and that the ecGCx is continuous. Panel D depicts the complete loss of the ecGCx by LAN staining in the hippocampus CA-1 regions of the BTBR ob/ob and note that the tight and adherens junction (TJ/AJ) remain intact (yellow arrows). The loss of the first barrier of the tripartite BBB may result in increased permeability. Images provided by CC 4.0 [52]. Magnification ×4000; scale bar = 0.5 μm in panels A and B. Magnification ×10,000; scale bar = 0.2 µm in panels C and D. ACfp = astrocyte foot process; Cl = capillary lumen; BEC = brain endothelial cell; HIP and HC = hippocampus CA-1 regions.