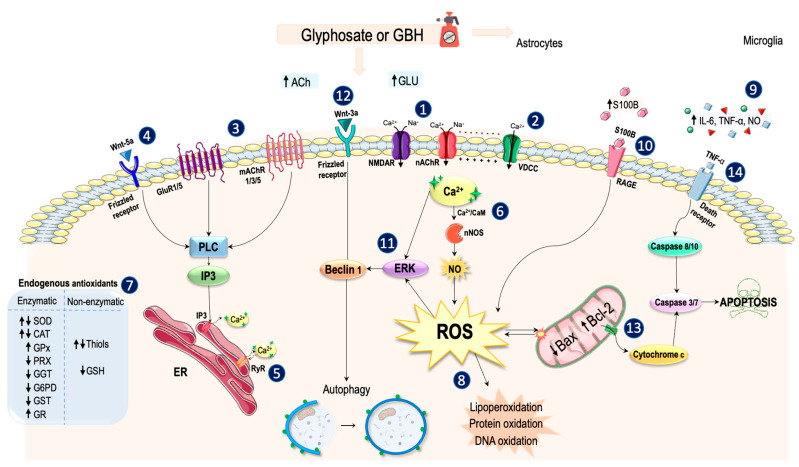
Figure 4.
Possible mechanism of action of glyphosate or GBH in the nervous system. The presence of glyphosate induces several changes, including (1) opening of nAChRs and NMDA receptors, as well as entry of Na+ and Ca2+ into the cell due to increased levels of ACh and GLU and/or the direct binding of glyphosate to the cavities of NMDAR; (2) opening of the VDCCs by cellular depolarization and entry of Ca2+; (3) activation of the metabotropic GLU and ACh receptors, which stimulate the PLC to generate IP3, which causes the release of Ca2+ from inside the ER; (4) increase in the levels of Wnt-5a, which binds to Frizzled receptors and triggers the generation of IP3, with the consequential release of Ca2+ from the interior of the ER; (5) Ca2+ binding to ryanodine receptors and Ca2+ release from inside the ER; (6) binding of Ca2+ to calmodulin and activation of nNOs, which releases NO; (7) modification of the activity and/or concentrations of endogenous antioxidants; (8) excessive levels of ROS, leading to oxidation of lipids, proteins, and DNA; (9) activation of glial cells, which release inflammatory cytokines and NO; (10) release of S100B protein, which binds to neuronal RAGEs and increases ROS overproduction; (11) activation of ERK due to excessive levels of Ca2+ and ROS, which activates Beclin 1 and induces autophagy; (12) increased levels of Wnt-3a, which binds to Frizzled receptors and induces autophagy; (13) mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to activation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway; and (14) binding of the ligand TNF-α to the death receptor, activating the extrinsic apoptosis pathway. Parts of the figure were created using templates from Servier Medical Art, which are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (http://smart.servier.com/ accessed on 17 February 2022). Abbreviations: GBH: glyphosate-based herbicide; GLU: glutamate; nAChR: nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; VDCC: voltage-dependent calcium channel; PLC: phospholipase C; IP3: inositol trisphosphate; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; CaM: calmodulin; nNOS: neuronal nitric oxide synthase; NO: nitric oxide; SOD: superoxide dismutase; CAT: catalase; GPx: glutathione peroxidase; PRX: peroxidase; GGT: gamma-glutamyl transferase; G6PD: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; GST: glutathione S-transferase; GR: glutathione reductase; GSH: glutathione; ROS: reactive oxygen species; IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha; S100B: S100 calcium-binding protein B; RAGE: receptor for advanced glycation end products; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ↑, increase; ↓, decrease.