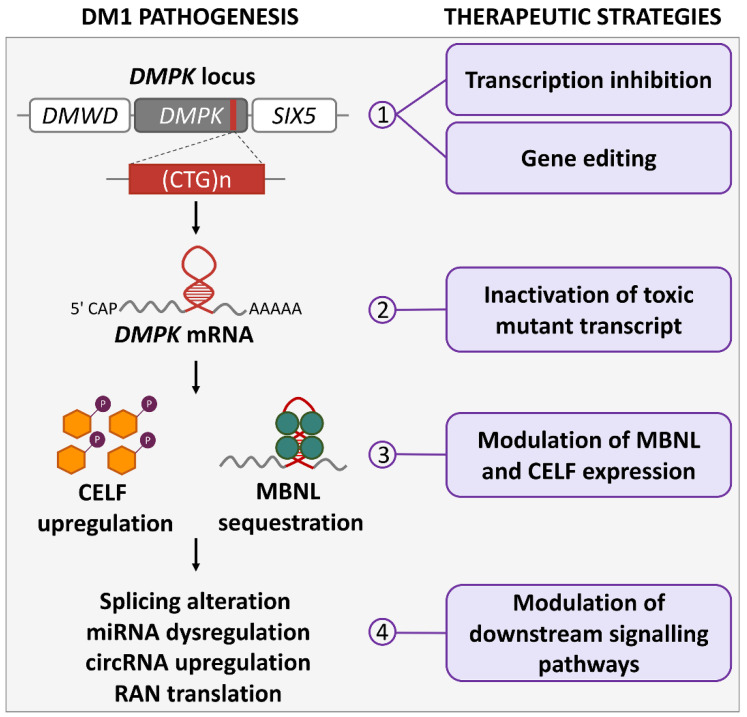
Figure 1.
DM1 pathogenetic mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. The actions of molecular therapies for DM1 at different pathogenetic levels are illustrated: (1) at DMPK gene, drugs can inhibit CTG-repeat transcription and induce repeat contraction; ZFN, TALEN or CRISPR/Cas9 nucleases can modify gene sequence by inducing CTG-repeat contractions or deletions, or by inserting premature polyadenylation signals; (2) mutated DMPK mRNA can be functionally inactivated by drugs inducing degradation or binding to CUG repeats; (3) MBNL can be released from CUG repeats by disruption of MBNL:CUG interaction through competitive binding, and CELF levels can be regulated by protein kinase C and glycogen synthase kinase 3β; (4) altered signaling pathways downstream of DMPK transcript can be rescued by modulation of splicing and miRNAs; circRNAs and RAN translation could also be targets of future therapies.