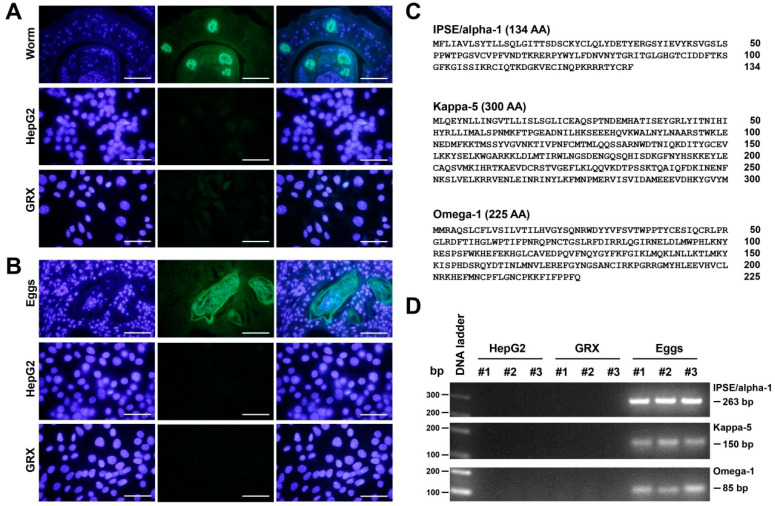
Figure 9.
Analysis of potential S. mansoni-specific glycostructures in GRX cells. (A) The monoclonal antibody 54-4C2 produced against the schistosome gut-associated circulating anodic antigens (CAA) [50] was used to stain GRX cells (lower panel). HepG2 cells served as negative control (middle panel), while sections of the gut of the adult worm were used as a positive control (upper panel). (B) The glycan-binding monoclonal antibody 128-1E7 that binds with high affinity to a broad range of proteins containing cercarial O- and GSL-glycans and to a selection of cercarial N-glycans that all contain abundantly fucosylated glycans [51] was used to stain GRX cells. Although this antibody failed to recognize any epitopes on GRX (lower panel) and HepG2 (middle panel), the antibody-stained antigens that are expressed on the eggs in hepatic granuloma of bisex-infected mice (upper panel). Original magnifications in (A,B) are 1000×. The scale bars correspond to 50 µm. (C) Protein sequences of the major antigenic glycoproteins IPSE/alpha-1, Kappa-5 and Omega-1 from S. mansoni. Amino acid positions are given on the right margin. The protein sequences were taken from GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) entries deposited under access. nos. XM_018799269.1, AY903306.1, and DQ013207 (accession date: 15 April 2022). (D) RNA from HepG2 cells, GRX cells, and from S. mansoni-infected mouse liver was subjected to RT-qPCR. Specific amplicons for IPSE/alpha-1, Kappa-5 and Omega-1 were only produced from S. mansoni infected mouse liver. Primer combinations used for this analysis are given in the Material and Method section (see Section 2.6).