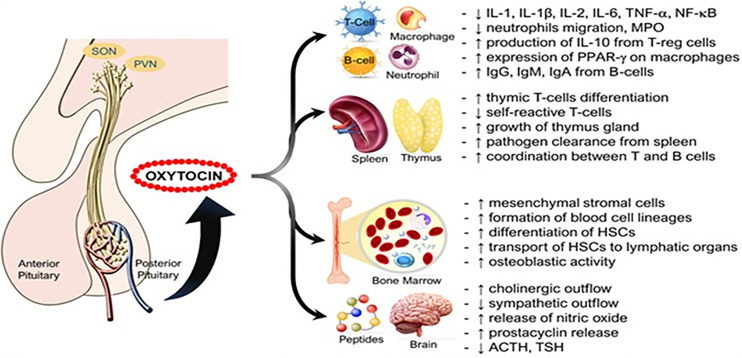
Figure 2.
Immune functions of oxytocin. Oxytocin acts peripherally on immune cells, immune organs (thymus, spleen, bone marrow), and centrally on the nervous system to modulate its immunogenic effects. ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; HSCs, hematopoietic stem cells; Ig, Immunoglobulin; IL, interleukin; MPO, myeloperoxidase; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; SON, supraoptic nucleus; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone. Other annotations are the same as Figure 1 [Figure originates and adapted from articles (57–59)]. Up arrow (↑) symbol indicates increase, whereas down (↓) arrow symbol indicates decrease in the effect mentioned.