Figure 2.
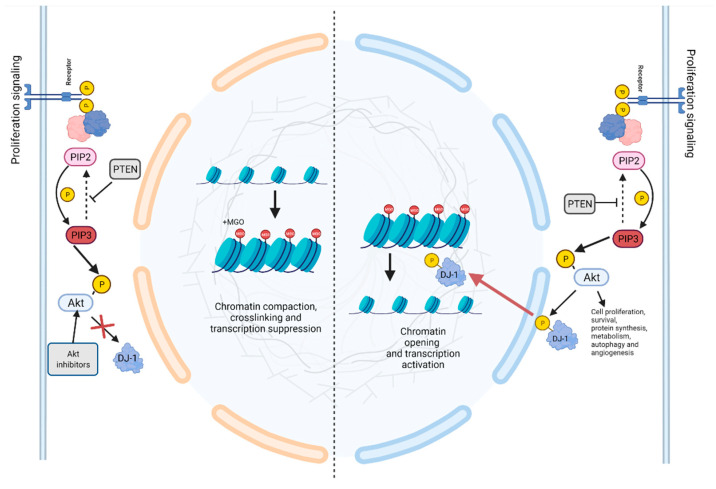
Role of DJ-1 during dicarbonyl stress. In senescent cells, the hyper-glycolitic phenotype induces dicarbonyl stress. Left side: In cells treated with Akt inhibitor, DJ-1 does not undergo phosphorylation. Unphosphorylated DJ-1 loses its glyoxalase activity and is unable to counteract the formation of MGO adducts, accounting for chromatin destructuration. Right side: In proliferating cell, under the activation of the Akt pathway, DJ-1 undergoes phosphorylation and translocates into the nucleus where it acts as glyoxalase. This activity preserves the histones code and the malignant proliferative potential.