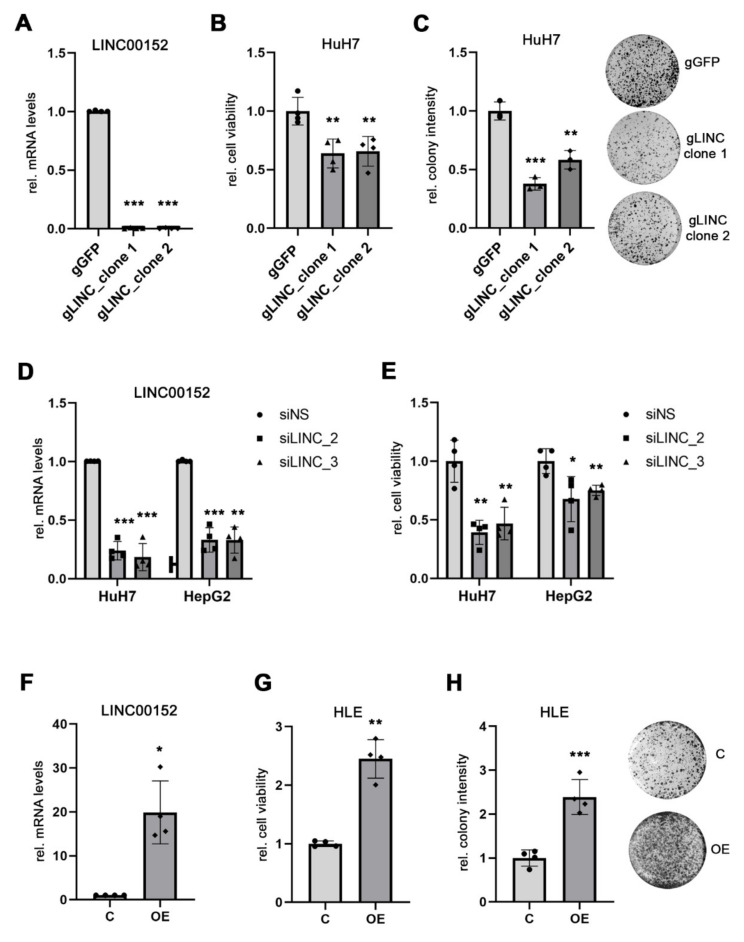
Figure 1.
LINC00152 expression affects cell viability of human HCC cell lines. (A) HuH7 cells 0 were engineered with CRISPR/Cas9 technology to achieve a complete LINC00152 gene knock-out (HuH7ΔLINC00152). (B) Reduced cell viability of HuH7ΔLINC00152 clones compared to gGFP control cells. (C) Clonogenicity was significantly impaired in HuH7ΔLINC00152 clones compared to control cells. (D,E) Efficient siRNA-mediated LINC00152 knockdown decreased cell viability of HuH7 and HepG2 cells. (F) Overexpression of LINC00152 in HLE cells transfected with pLV-LINC00152 plasmid. (G) LINC00152 overexpression increased the cell viability of HLE cells compared to cells transfected with an empty vector. (H) Increased colony formation of LINC00152-overexpressing cells compared to control cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD of at least 3 independent experiments. Student t-test was used in (A–C,F), while Welch’s t-test in (D,E): * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Abbreviations: gGFP, guide RNA targeting GFP; gLINC, guide RNA targeting LINC00152; siNS, scrambled, nonsense siRNA; siLINC_2/_3, siRNA 2 and 3 specifically targeting LINC00152; C, control cells transfected with empty vector; LINC00152 OE, LINC00152 overexpression; OE, overexpression; rel., relative.