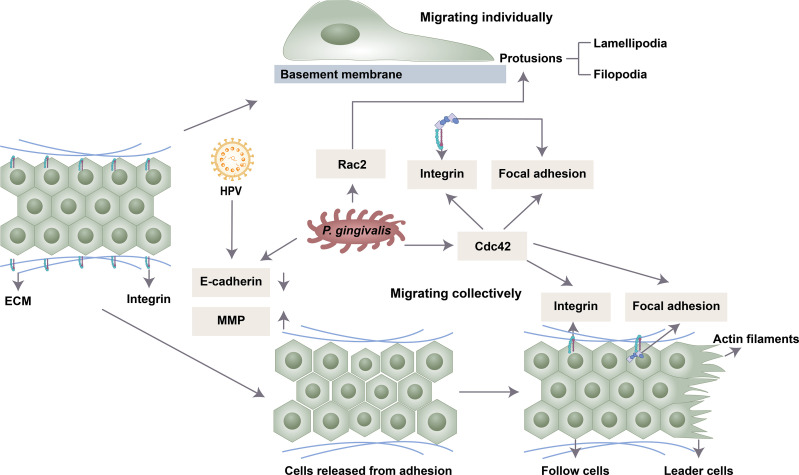
Figure 1.
Possible mechanisms by which oral microbiota influence cell migration. P. gingivalis and HPV 16 release intercellular adhesions by downregulating E-cadherin and upregulating MMP. P. gingivalis enhances the expression of Cdc42 and Rac2 to induce the front and back polarity that is crucial for cell migration. P. gingivalis drives cell clusters to move orientally through the formation of integrin and focal adhesion.