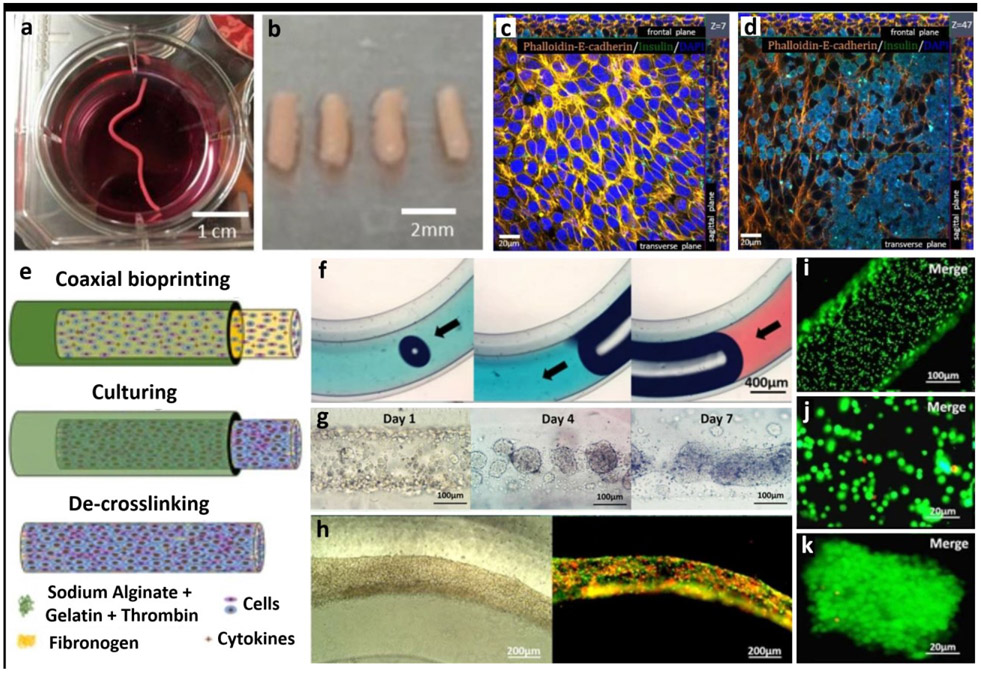
Figure 6:
Scaffold-free fabrication of tissue models. (a-b) Fabrication of tissue strands made of rat dermal fibroblasts (RDFs), (c-d) which were then further cultured with beta-TC-3 insulinoma cells. Beta-TC-3 cells adhered on top of RDF strands showing positive to insulin in the outer layer of strands. Adapted with permission from Reference [84]. e) Schematic for the fabrication steps of multicellular heterogeneous tumor fibers: coaxial bioprinting, in vitro culturing and de-crosslinking. f) Integrity and continuity testing of the fiber by passing dye through the filament – no leaks is indicative of a continuous fiber. g) Images of the cultured tumour fibers after 1, 4 and 7 days, h) tumor/stroma cell fibers traced with RFP/GFP - cell fibers composed of GFP-expressing MSCs and RFP-expressing tumor cells after bioprinting and cultured over a period of 3 days, i-k) cell viability testing for the cell laden fibers immediately after bioprinting performed using LIVE/DEAD assay, h) Assessment of cell viability five days post bioprinting and culturing. Adapted with permission from Reference [87].