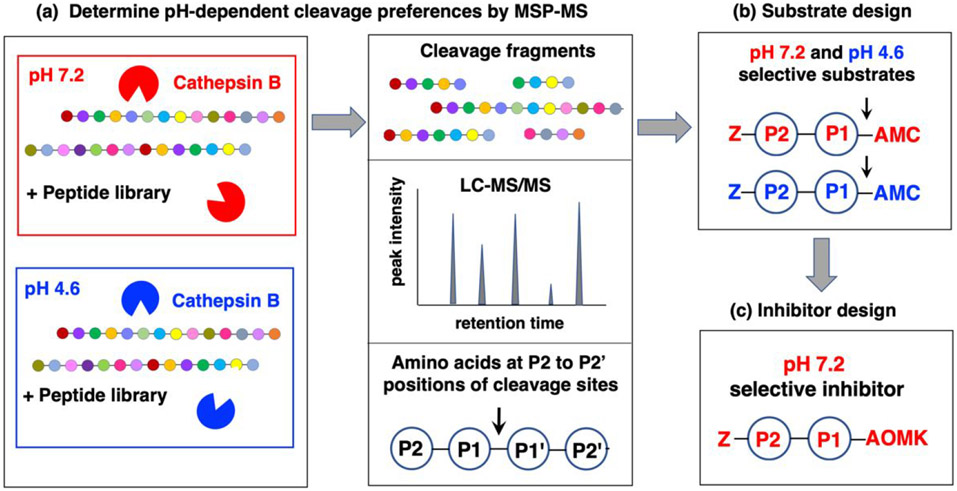
Figure 1. Workflow to analyze cathepsin B substrate cleavage site preferences for design of pH-selective inhibitors.
(a) Cathepsin B substrate cleavage properties assessed at pH 7.2 and pH 4.6 by multiplex substrate profiling by mass spectrometry (MSP-MS) analyses. The substrate cleavage profiles of cathepsin B at pH 7.2 and pH 4.6 were assessed by MSP-MS analyses. Cathepsin B was incubated (at room temperature, for 15 and 60 minutes) at pH 7.2 and pH 4.6 with the peptide library consisting of 228 14-mer peptides designed to contain all neighbor and near-neighbor amino acid combinations. Peptide cleavage products were identified and quantitated by LC-MS/MS analyses. The frequencies of amino acid residues at the P2 to P2' positions of the P1-↓P1' cleavage sites were assessed.
(b) Design of pH selective peptide-AMC substrates. Substrates representing the preferred residues at P1 and P2 positions at pH 7.2 and pH 4.6 were utilized for development of pH selective peptide-AMC substrates of cathepsin B. These substrates contained a C-terminal 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (AMC) reporter group and an N-terminal carboxybenzyl (Z) group
(c) Design of pH selective peptidic inhibitors. Peptide-AOMK inhibitors were synthesized based on the AMC substrates that have high selectivity for cleavage at either pH 7.2 or pH 4.6.