FIGURE 3.
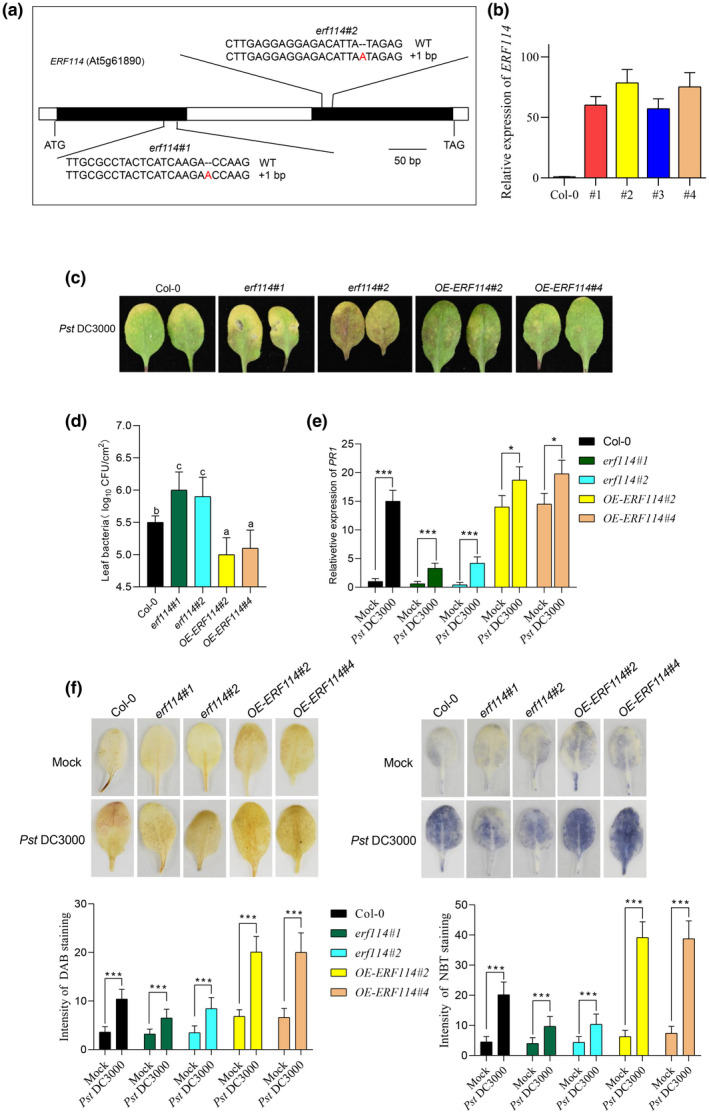
ERF114 contributes to Arabidopsis disease resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst) DC3000. (a) Construction of CRISPR/Cas9‐based erf114 knockout transgenic lines. Two sgRNA sequences that specifically target ERF114 were used, generating two mutants, erf114#1 and erf114#2, both with an “A” insertion (indicated in red font). (b) Relative expression level of ERF114 in four‐week‐old transgenic lines overexpressing ERF114 (OE‐ERF114) and wild‐type Col‐0 leaves. UBC21 was used as the internal control. Data represent the ratio of ERF114 expression between OE‐ERF114 plants and wild‐type Col‐0. The bars were calculated based on three independent experiments. The values are mean ± SD (n = 3). (c) Typical Pst DC3000 disease symptoms in Col‐0, erf114#1, erf114#2, OE‐ERF114#2, and OE‐ERF114#4 leaves. Four‐week‐old leaves were inoculated with Pst DC3000 bacterial suspension or 10 mM MgCl2. Photographs were taken at 48 h postinoculation (hpi). (d) Bacterial growth in Col‐0, erf114, and OE‐ERF114 leaves. Bacteria were isolated from leaves at 48 hpi and counted with gradient dilution assays. Data from three separate experiments are shown (mean ± SD, n = 6). Different letters above the bars indicate statistically significant differences at p < 0.05 (one‐way analysis of variance, ANOVA). (e) Relative expression levels of PR1 in the leaves of 4‐week‐old wild‐type (Col‐0), erf114, OE‐ERF114 plants at 24 hpi. UBC21 was used as the internal control. Relative expression is indicated compared to the transcript level of UBC21. The bars were calculated based on three independent experiments. The values are mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, one‐way ANOVA. (f) Leaves were inoculated with Pst DC3000 or 10 mM MgCl2 and stained with 3,3′‐diaminobenzidine (DAB) and nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) at 24 hpi. Photographs were taken (top) and H2O2 and superoxide anion accumulation was quantified in nine leaves by measuring the intensity of staining with ImageJ (bottom). ***p < 0.001, one‐way ANOVA
