FIGURE 3.
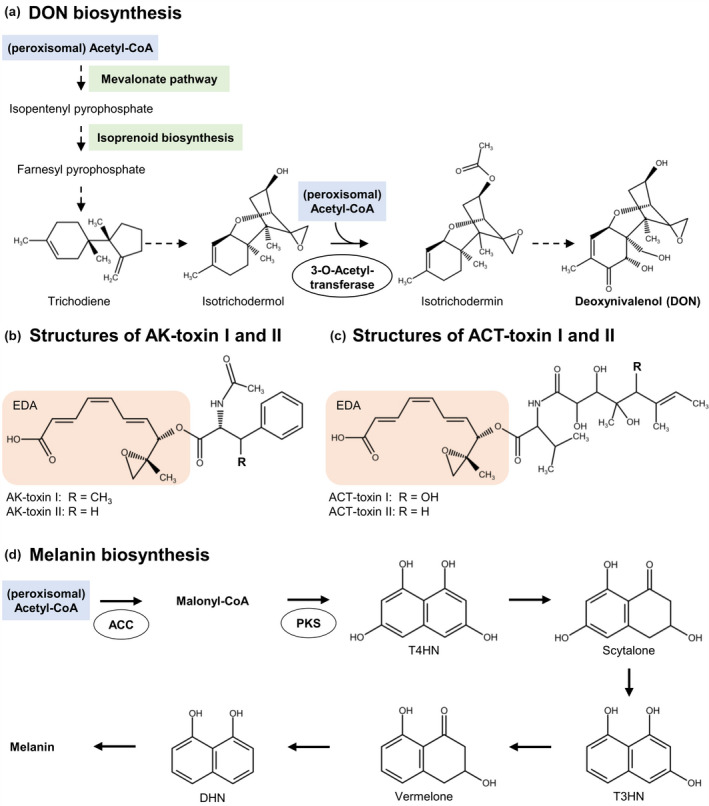
Peroxisomal functions in the biosynthesis of mycotoxins and melanin. (a) Biosynthesis of the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol (DON, [(3α,7α)‐3,7,15‐trihydroxy‐12,13‐epoxytrichothec‐9‐en‐8‐one]) from Fusarium graminearum requires peroxisomal acetyl‐CoA at two important steps. (b) The structures of relevant AK toxins of Alternaria species are shown. AK toxin I ((2E,4Z,6E)‐8‐(2‐acetamido‐3‐phenylbutanoyl)oxy‐8‐(2‐methyloxiran‐2‐yl)octa‐2,4,6‐trienoic acid) is very similar to AK toxin II. (c) ACT toxins I and II are AK toxin derivatives. The orange boxes indicate the common moiety of 9,10‐epoxy‐8‐hydroxy‐9‐methyl‐decatrienoic acid (EDA). (d) DHN‐melanin is synthesized by the polyketide pathway in filamentous fungi. ACC, acetyl‐CoA carboxylase; DHN, 1,8‐dihydroxynaphthalene; PKS, polyketide synthase; T3HN, 1,3,8‐trihydroxynaphthalene; T4HN, 1,3,6,8‐tetrahydroxynaphthalene
