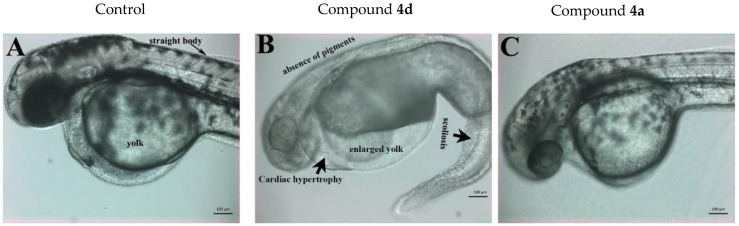
Figure 8.
Representative live images of zebrafish embryos at 48 hpf. (A) Mock (0.5% V/V)-treated zebrafish embryos developed normally. The embryos had normal circulation (shown separately in videos) and the body and eyes were fully pigmented. They had a normal yolk size and their bodies were also straight. (B) Zebrafish embryos treated with compound 4d (sublethal dose of 0.76 µM shown here). The embryos showed multiple teratogenic defects in response to exposure to compound 4d, including scoliosis (bent spine and body), no pigmentation, an enlarged yolk and cardiac hypertrophy. (C) The zf embryos treated with compound 4a (15.88 µM) showed the same phenotype as the mock-treated embryos, with full pigmentation, no sign of cardiac hypertrophy and straight bodies. However, the treated embryos did not have active circulation (shown in supplementary videos). The scale bar represents 100 µm and the images were taken under the same magnification.