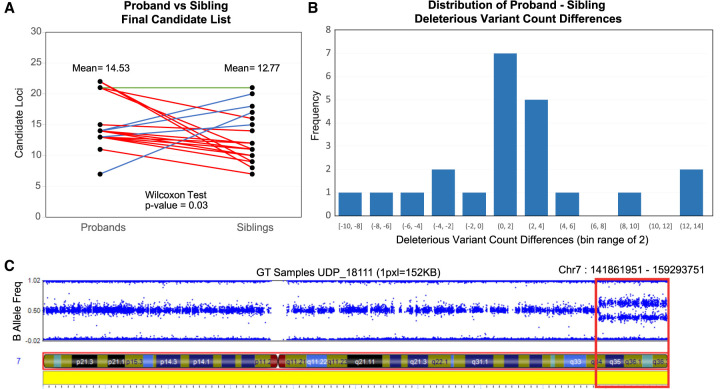
Figure 4.
Proband-sibling pairwise candidate analysis results on 15 nuclear families of at least quartet in size, comprising a population of 15 probands and 22 siblings. Plot A shows the average number of candidate variants between the probands and sibling populations. Seventeen red lines (four overlapping) represent proband-sibling pairs where the proband has more DVs than their matched sibling, five blue lines (one overlapping) represent probands that have less DVs than their matched sibling, and one green line, where probands have the same number of DVs as their matched sibling. The proband population holds an average of 14.53 DVs whereas the sibling population has an average of 12.77 DVs. A one-tailed Wilcoxon signed-rank test of the hypothesis that the probands have greater numbers of DVs than their matched siblings produced a P-value of 0.0333. (B) The distribution of proband-sibling DV list size differences. (C) A mosaic region identified by the workflow (red box) overlaid with the SNP-chip B allele frequency plot for a UDP sample.