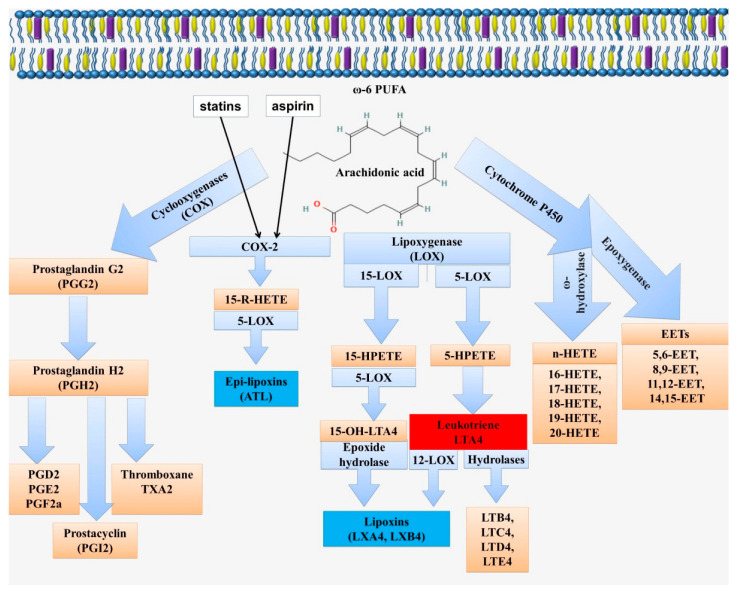
Figure 3.
Scheme of biosynthesis of lipid mediators from arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid can be metabolized via the cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygenase (LOX), or cytochrome P 450 pathways (CYP). Enzymatic conversion through the COX pathway leads to the formation of prostaglandins (PG). The LOX pathway is associated with the formation of lipoxins (LX) and leukotrienes (LT) via 5-LOX, 12-LOX, and 15-LOX. This pathway includes the formation of the intermediate metabolites 5-/15-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-/15-HpETE) and 5-/15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-/15-HETE). The ω-hydroxylase activity of CYP enzymes leads to the formation of hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (16-, 17-, 18-, 19-, and 20-HETE). The epoxygenase activity of CYP enzymes is associated with the formation of arachidonic acid epoxides or epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs; 5,6-EET, 8,9-EET, 11,12-EET and 14,15-EET), known as endothelial-derived hyperpolarizing factors.