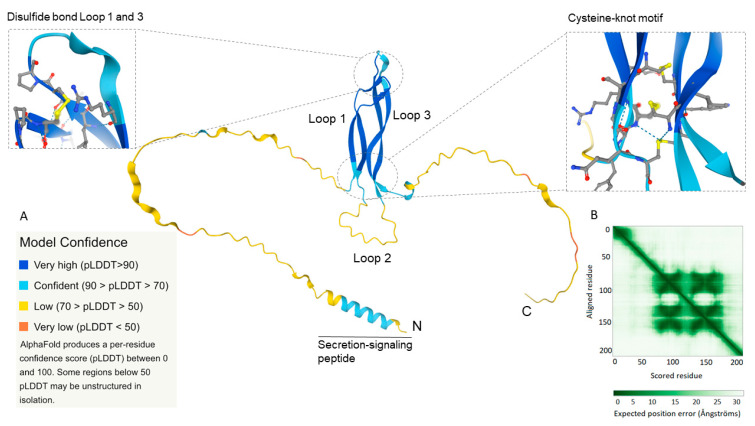
Figure 4.
The three-dimensional structure of human sclerostin was generated from the amino acid sequence in the novel AlphaFold Protein Structure Database (https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/Q9BQB4) (accessed on 19 September 2021) [58]. The protein comprises a core structure of loops 1 and 3, each having two anti-parallel running β-sheets linking with three disulfide bonds (cysteine-knot motif, magnification to the right; disulfide bond in yellow) and one disulfide bond in the top (magnification to the left; disulfide bond in yellow). Sclerostin contains also a flexible second loop in the bases and two N- and C-terminal spacer arms. (A) Confidence score (0–100) of model accuracy based on per-residue predicted local-distance difference test (pLDDT). Loops 1 and 3 have a high to very high confidence score (pLDDT > 70) and loop 2 and the spacer arms low confidence score (pLDDT < 70). (B) Expected position error, showing the possible interaction/proximity between the residues, depending on the distance between each residue (in Ångströms). Sclerostin has four closely aligned inner-sequence core domains, each containing one β-sheet.