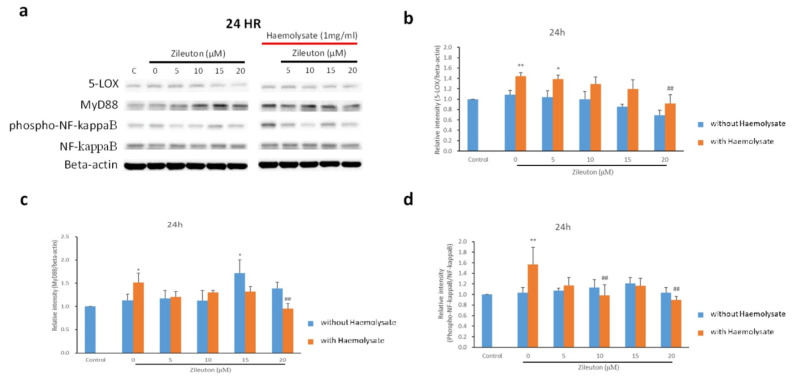
Figure 4.
Western blot results for 5-LOX, MyD88, and phosphor-NF-κB (pNF-κB)/NF-κB. (a) Western blot results for 5-LOX, MyD88, and pNF-κB/NF-κB. (b) Histogram illustrating the Western blot results for 5-LOX expression level. The x-axis represents the control group, haemolysate + vehicle, and haemolysate + different concentrations of zileuton; the y-axis represents the expression levels as the relative intensity of protein bands that appeared in the Western blot assay. The haemolysate + vehicle group and the haemolysate + 5 μM zileuton group showed a higher expression level of 5-LOX than the control group. The expression of 5-LOX in the haemolysate + 20 μM zileuton group was significantly lower than that in the haemolysate + vehicle group (p < 0.01). There was no significant difference between the haemolysate + 20 μM zileuton group and the control group. The haemolysate-induced overexpression of 5-LOX can therefore be inhibited by a high concentration (20 μM) of zileuton (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with control; ## p < 0.01 compared with haemolysate + vehicle group, n = 3). (c) Histogram illustrating the Western blot results for MyD88. The haemolysate + vehicle group displayed a significantly higher expression level of MyD88 than the control group (p > 0.05). The expression level of MyD88 in the haemolysate + 20 μM zileuton group was significantly lower than that in the haemolysate + vehicle group (p < 0.01). There was no significant difference between the haemolysate + 20 μM zileuton group and the control group (* p < 0.05 compared with control; ## p < 0.01 compared with haemolysate + vehicle group, n = 3) (d) Histogram illustrating the pNF-κB/NF-κB ratio determined via Western blot assay. The activated NF-κB, i.e., pNF-κB, enhances the production of downstream pro-inflammatory cytokines. Herein, we measured the pNF-κB/NF-κB ratio via Western blot assay to determine the activation level of NF-κB, which is directly proportional to the pNF-κB/NF-κB ratio. The haemolysate + vehicle group had a significantly higher pNF-κB/NF-κB ratio than the control group (p < 0.01), while the haemolysate-exposed BV-2 cells treated with 10 and 20 μM of zileuton showed a significantly lower pNF-κB/NF-κB ratio than those treated with the vehicle (p < 0.01). However, there was no significant difference between the haemolysate + 10 μM and + 20 μM zileuton and the control groups (** p < 0.01 compared with control; ## p < 0.01 compared with haemolysate + vehicle group, n = 3).