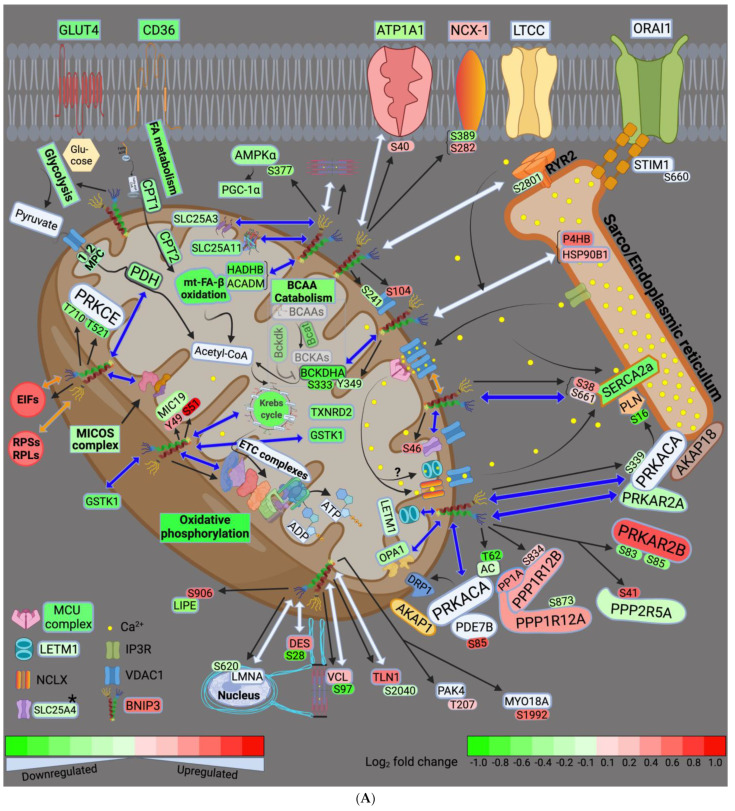
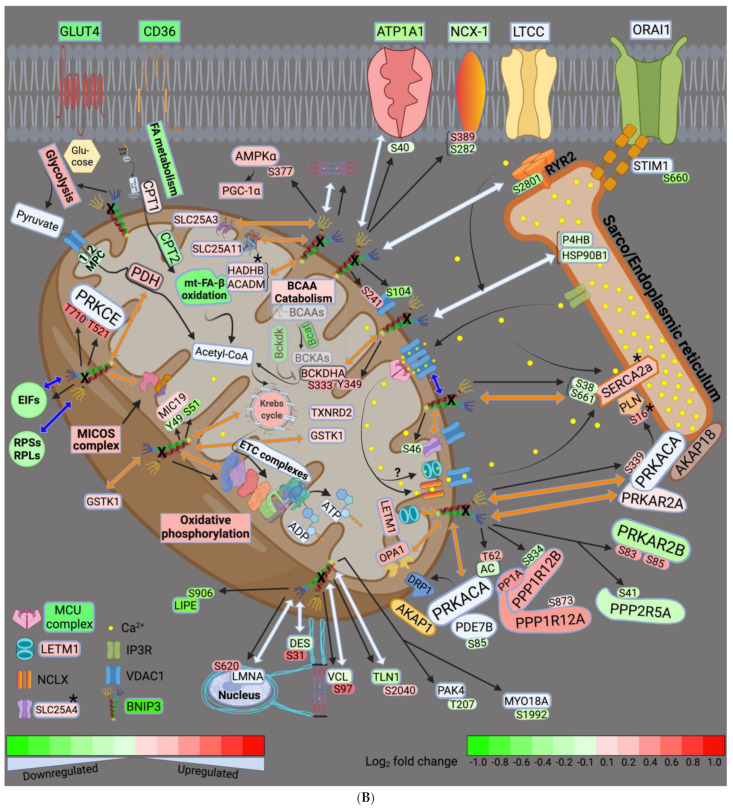
Figure 8.
Schematic drawings highlight some of the key findings of the effect of BNIP3 knockdown in the rat pressure overload HFrEF model. These are presented as ShL vs. Sham (A) and ShB vs. ShL (B). The green and red color intensities show the degree of downregulation and upregulation of activity, respectively, or the log2-fold change in protein or phosphosite expression, as noted by the scale bar at the bottom right side of the schematic drawing. The double-headed arrows show the interaction between BNIP3 and its interacting protein. The blue and orange colors show whether there was inhibition/downregulation or activation/upregulation as a result of this interaction. The straight black arrows point to an effect of BNIP3 on protein phosphorylation. The black asterisk denotes changes in protein expression or phosphorylation by western blot only. Abbreviations: GLUT4, glucose transporter member 4; CD36, platelet glycoprotein 4; NCX1, sodium/calcium exchanger 1; LTCC, voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel; ATP1A1, sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-1; STIM1, stromal interaction molecule 1; ORA1, calcium release-activated calcium channel protein 1; AMPK, 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; CPT1 and 2, carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase 1 and 2; SLC25a3, mt-phosphate carrier protein; SLC25a11, mt-2-oxoglutarate/malate carrier protein; SLC25a4, ADP/ATP translocase 1; HADHB, mt-trifunctional enzyme subunit beta; FA, fatty acid; Bckdk, mt-3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase kinase; BCAA, branched-chain amino acid; Bcat, BCAA aminotransferase; BCKAs, branched-chain α-ketoacids; BCKDHA, mt-2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase subunit alpha; GSTK1, glutathione S-transferase kappa 1; TXNRD2, mt-thioredoxin reductase 2; BNIP3, BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3; VDAC1, voltage-dependent anion channel isoform 1; IP3R, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor; NCLX, mt-sodium/calcium exchanger; LETM1, mt-proton/calcium exchanger; MCU, mt-calcium uniporter; P4HB, protein disulfide isomerase; HSP90B1, heat shock protein 90 beat member 1; SERCA2a, sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2a; PLN, phospholamban; RYR2, ryanodine receptor isoform 2; PRKACA, cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha; PRKAR2A, cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-alpha regulatory subunit; PRKAR2B, cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-beta regulatory subunit; AKAP1 and 18, A-kinase anchor protein 1 and 18; AC, adenylate cyclase; PP1A, serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1-alpha catalytic subunit; PPP1R12A and PPP1R12B, PP1 regulatory subunits 12A and 12B; PDE7B, cAMP-specific 3′,5′-cyclic phosphodiesterase 7B; DRP1, dynamin-related protein 1; OPA1, optic atrophy 1; PRKCE, protein kinase C epsilon type; ETC, electron transport chain; MICOS, mt-contact site and cristae organizing system; MIC19, MICOS complex subunit MIC19; EIFs, eukaryotic translation initiation factors; RPSs, 40S ribosomal proteins; RPLs, 60S ribosomal proteins; LIPE, hormone sensitive lipase; DES, desmin; LMNA, lamin A; VCL, vinculin; TLN1, talin-1; PAK4, serine/threonine protein kinase PAK 4; MYO18A, unconventional myosin-XVIIIa.