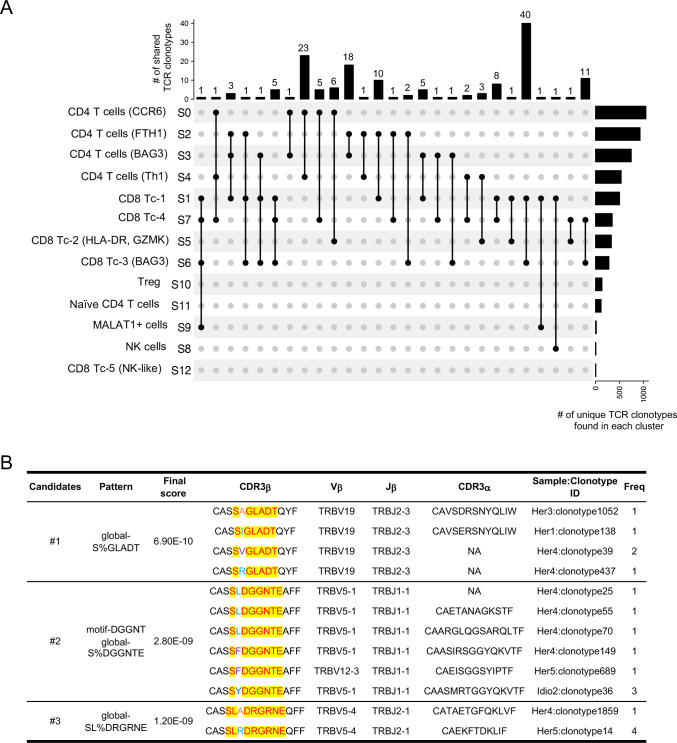
Figure 4.
Single-cell RNA sequencing/TCR-sequencing uncovers unique interactions among T-cell lineages and shared antigen binding motifs in CP. (A) Upset plots displaying TCR clonotypes shared among T-cell clusters from T cells across control and CP groups. Each shared clonotype was indicated by black dots with a connected black line. The horizontal bar graph indicates the total number of shared TCR clonotypes for cluster intersections, and the vertical bar graph indicates the number of unique clonotypes found in a single cluster. (B) Representative TCR specificity groups and potential antigen binding motifs by GLIPH2 cluster analysis of TCR CDR3β sequences from pancreatic T cells across control, hereditary and idiopathic CP. Candidates were selected from the clusters with a final score of less than 10−8 and shared by at least two different individuals. CP, chronic pancreatitis; TCR, T-cell receptor.