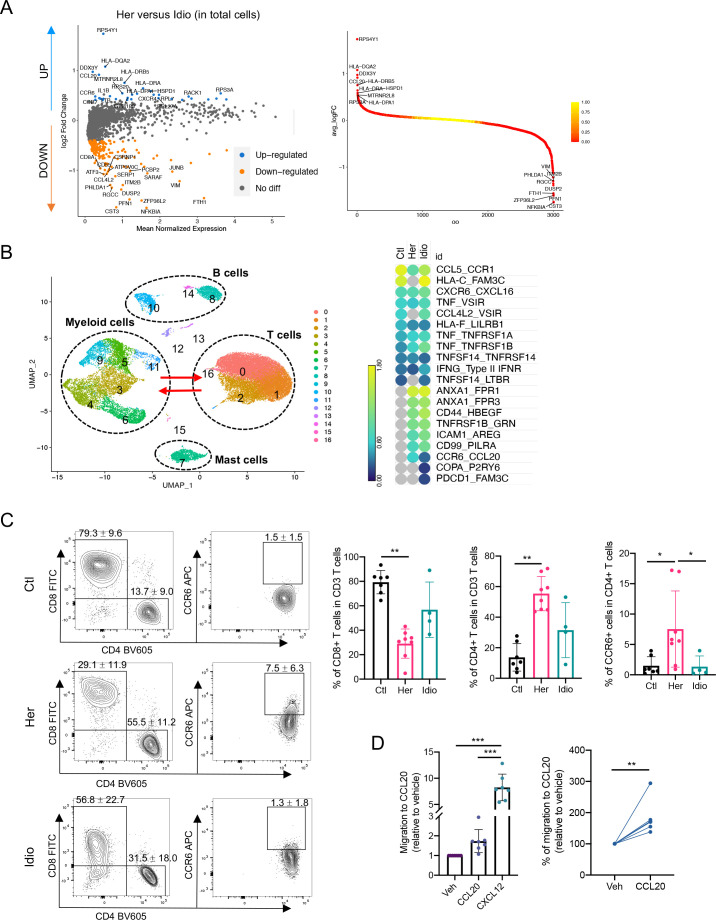
Figure 6.
Functional analysis implicates the CCR6-CCL20 axis as hereditary CP-specific pancreatic immune crosstalk. (A) Volcano plot of DEG analysis between hereditary and idiopathic CP groups with total immune populations. Each dot represents a gene, with significantly upregulated top 20 genes and downregulated top 20 genes in hereditary CP versus idiopathic CP coloured blue and yellow, respectively (left). DEGs ranked by fold changes in hereditary CP versus idiopathic CP (right). (B) UMAP plot of total pancreatic immune cells (left). Heatmap of combined expression of selected cytokine/chemokine and their receptor displaying the interactions between myeloid cells and T cells discovered by CellPhoneDB (right). (C) Flow cytometry analysis of CD8+, CD4+ or CCR6+ CD4+ T cells (Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01). (D) Chemotaxis assay with pancreatic immune cells from hereditary CP (left, one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; right, paired t-test; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). CP, chronic pancreatitis; Ctl, control; DEG, differentially expressed genes; Her, hereditary; Idio, idiopathic; UMAP, uniform manifold approximation and projection.