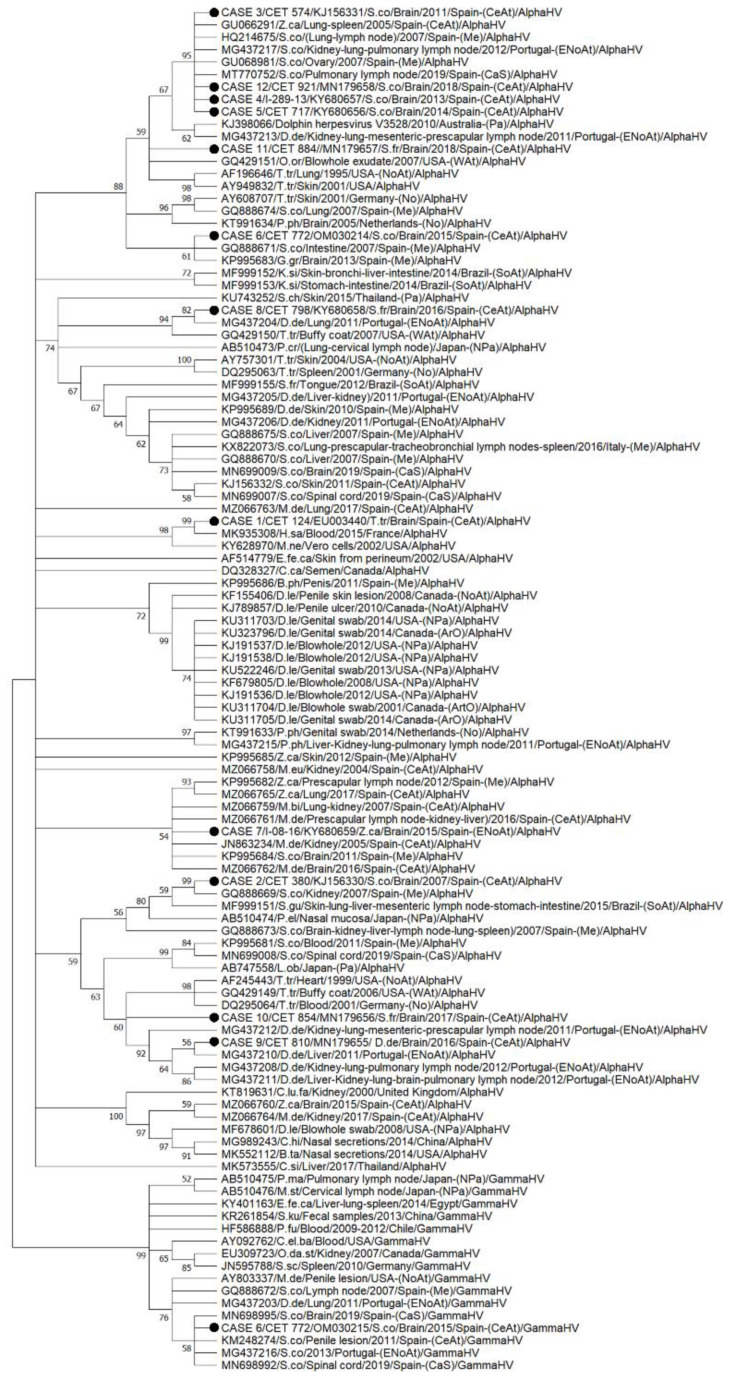
Figure 8.
Nucleotide phylogenetic tree representing the relationships among cetaceans HVs. The phylogenetic tree was based on the herpesvirus DNA polymerase gene and constructed using the Tamura 3-parameter model (T92 + G) Maximum likelihood (ML), with an estimate of statistical support from 500 bootstrap replicates. Bootstrapping values are indicated as percentages next to the bifurcations (BVs less than 50 were collapsed into a polytomy). The name of each sequence includes the GenBank accession number (when available), cetacean species (B.ph, Balaenoptera physalus; D.le, Delphinapterus leucas; D.de, Delphinus delphis; G.gr, Grampus griseus; K.si, Kogia sima; L.ob, Lagenorhynchus obliquidens; M.de, Mesoplodon densirostris; O.or, Orcinus orca; P.cr, Pseudorca crassidens; P.el, Peponocephala electra; P.ph, Phocoena phocoena; S.ch, Sousa chinensis; S.co, Stenella coeruleoalba; S.fr, Stenella frontalis; S.gu, Sotalia guianensis; T.tr, Tursiops truncatus; and Z.ca, Ziphius cavirostris), the year, the geographic area of the stranding (BeS, Bering Sea; CEAt, Central Eastern Atlantic Ocean; In, Indian Ocean; Me, Mediterranean Sea; NEAt, Northeast Atlantic Ocean; Npa, North Pacific Ocean; NS, North Sea; NWAt, Northwest Atlantic Ocean; Pa, Pacific Ocean; SEAt, South Eastern Atlantic Ocean), and the tissues in which they were detected. Herpesviruses sequences from other species incorporated to the phylogenetic analysis included terrestrial and flying mammals (B.ta, Bos taurus; C.lu.fa, Canis lupus familiaris; C.hi, Capra hircus; C.ca, Cervus canadensis; C.el.ba, Cervus elaphus barbarous; E.fe.ca, Equus ferus caballus; H.sa, Homo sapiens; M.ne, Macaca nemestrina; O.da.st, Ovis dalli stonei; P.fu, Pseudalopex fulvipes; S.ku, Scotophilus Kuhlii; S.sc: Sus scrofa) and reptiles (C.si, Crocodylus siamensis).