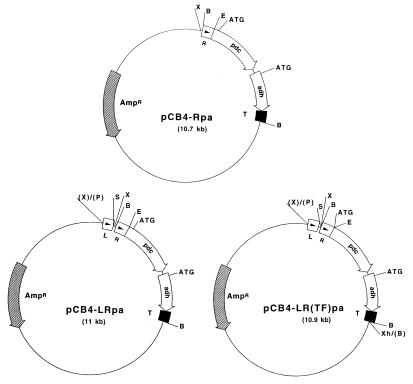
FIG. 1.
Plasmid vectors for expressing Z. mobilis PDC (pdc) and ADH II (adh) in cyanobacteria. All of the plasmids were constructed in the shuttle vector pCB4 for transforming Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. In pCB4-Rpa, the pdc and adh genes are under the control of the promoter of the rbcLS operon (labelled R). In both pCB4-LRpa and pCB4-LR(TF)pa, pdc expression and adh expression are driven by a combination of the rbcLS promoter and the E. coli lac promoter (labelled L). The ribosome-binding site and the start codon of the rbcL gene were fused in frame to the second codon of the pdc gene in pCB4-LR(TF)pa. The arrows indicate the directions of transcription and translation. The position of the effective translation initiation codon (ATG) for the pdc and adh genes is indicated. The transcription terminator sequence of the adh gene is represented by a solid box (labelled T). The restriction sites used in cloning are shown (B, BamHI; P, PvuII; E, EcoRI, S, SalI; X, XbaI; Xh, XhoI). Letters in parentheses indicate restriction sites which were eliminated by blunt end ligation.