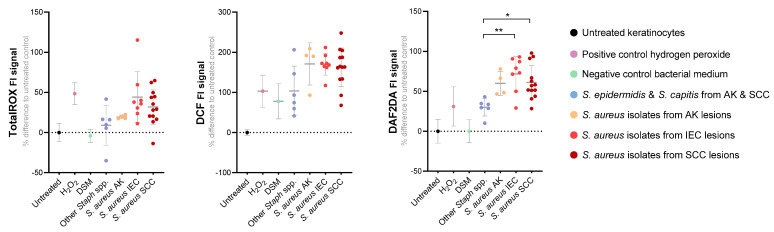
Figure 4.
Exposure to S. aureus secretome increases intracellular reactive oxygen and nitrosative species in human keratinocytes. The level of intracellular reactive oxygen/nitrogen species after 6 h treatment with secretome from S. aureus isolated from actinic keratosis (AK, n = 4), intraepithelial carcinoma (IEC, n = 8) or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC, n = 13), was measured in primary human keratinocytes using three different fluorescent probes. The positive control was hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and negative controls included untreated cells, S. aureus culture media (DSM) and secretome from other Staphylococcus species derived from AK and SCC (S. epidermidis, S. capitis). Displayed is the relative fluorescent signal (as percentage difference from the untreated control) for the TotalROX probe measuring peroxyacids, free radicals, singlet oxygen and nitrosative species, DCF-DA probe measuring hydroxyl and peroxyl radicals and DAF-2 DA probe, a nitric oxide indicator. Each dot represents a different bacterial isolate and shows the grouped mean value from three independent experiments, each performed in technical triplicates. Dunn’s multiple comparisons test was performed between groups S. aureus AK, IEC, SCC and other Staphylococcus spp. for each assay (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01).