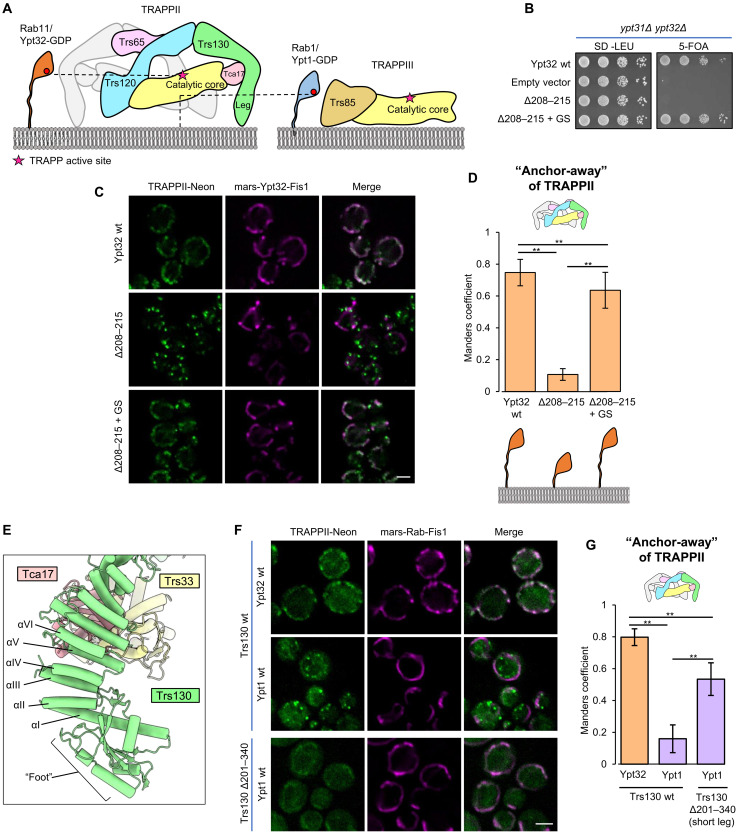
Fig. 4. The Trs130 leg enforces counterselection against Rab1 by steric gating.
(A) Schematic illustrating the steric gating mechanism, in which the Rab1 HVD is not long enough to enable access to the TRAPPII active site. (B) Complementation test assessing the effects of Rab11/Ypt32 HVD truncation and residue substitution on cell viability. (C) GRab-IT imaging data to test the interaction of TRAPPII with the same Rab11/Ypt32 constructs tested in (B). (D) Quantitation of the data in (C). (E) View of the Trs130 leg structure. (F) GRab-IT imaging data to test the interaction of Rab11/Ypt32 with TRAPPII harboring the short-leg Trs130 construct. (G) Quantitation of the data in (F). Scale bars, 2 μm (C and F). **P < 0.01.