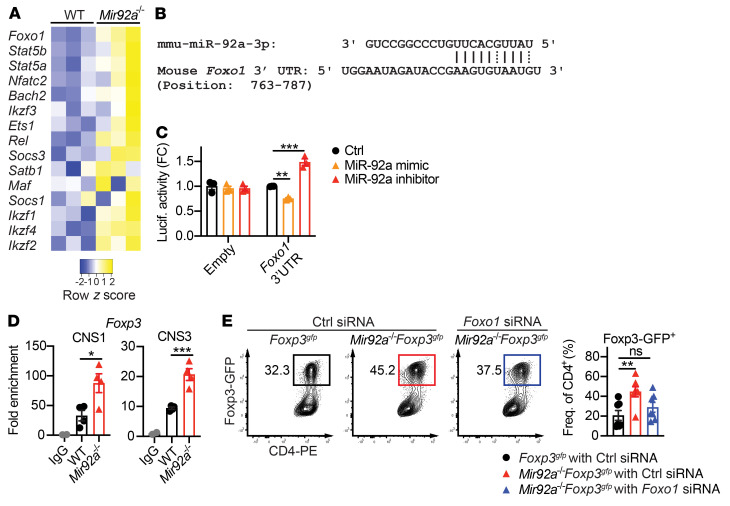
Figure 3. miR-92a inhibits Treg differentiation by targeting Foxo1.
(A) Heatmap showing qPCR analyses of selected Treg/Th17-associated transcription factors in Treg-polarized WT and Mir92a–/– naive CD4+ T cells (n = 3). (B) In silico prediction analysis of complementary binding between miR-92a and the Foxo1 3′-UTR. (C) Luciferase activity in a HEK293T cell line cotransfected with luciferase plasmid containing no insert (empty) or a Foxo1 3′-UTR sequence, along with either LNA control (Ctrl), a miR-92a mimic, or a miR-92a inhibitor (n = 3). (D) ChIP analyses of Foxo1 binding to Foxp3 CNS1 or CNS3 loci in Treg-polarized Foxp3gfp and Mir92a–/– Foxp3gfp naive CD4+ T cells (n = 4). Fold enrichment is shown relative to WT IgG conditions. (E) Representative flow cytometric plots and frequencies of Foxp3+ cells in Foxp3gfp and Mir92a–/– Foxp3gfp naive CD4+ T cells transfected with control or Foxo1 siRNA and cultured under Treg-polarizing conditions (n = 7). Data are representative of 2–3 independent experiments and indicate the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, by 1-way ANOVA with Dunnet’s multiple-comparison test (C and D) or Šidák’s multiple-comparison test (E).