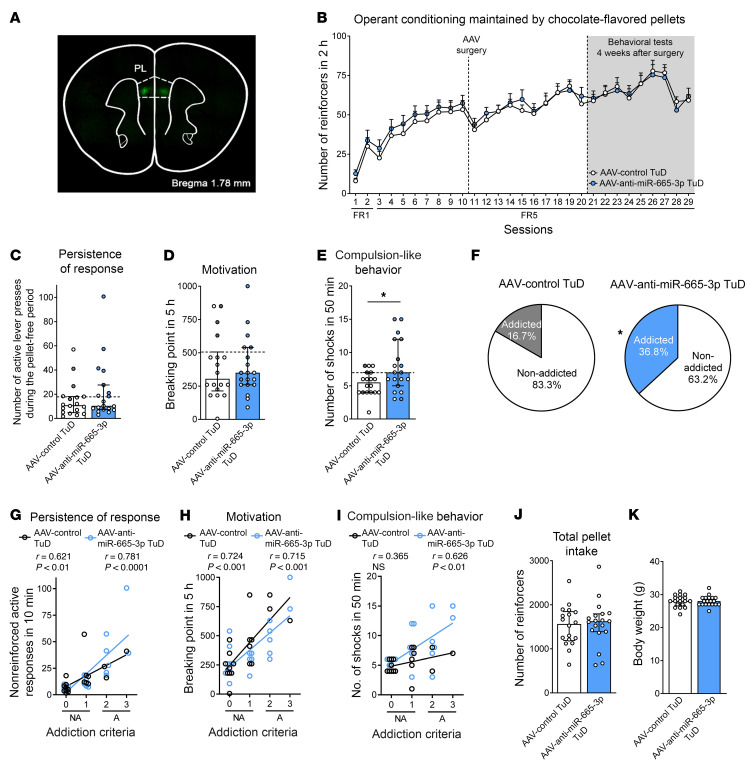
Figure 6. Functional validation of candidate mmu-miR-665-3p inhibition.
(A) Representative fluorescence images showing virus-dependent GFP protein expression at the PL injection site. (B) Number of reinforcers during operant training sessions maintained by chocolate-flavored pellets comparing AAV control TuD mice and AAV–anti–mmu-miR-665-3p TuD mice. (C–E) Behavioral tests for the 3 addiction-like criteria showed increased compulsion-like behavior in mice with mmu-miR-665-3p inhibition (individual values with the median and IQR are shown; Student’s t test, *P < 0.05). Addicted mice are indicated by filled circles. (F) Increased percentage of mice with mmu-miR-665-3p inhibition classified as food-addicted animals (χ2 test, *P < 0.05). (G–I) Pearson’s correlations between individual addiction-like criteria and (G) nonreinforced active responses in a 10-minute period, (H) the breaking point in 5 hours, (I) the number of shocks in a 50-minute period, (J) pellet intake, and (K) body weight (n = 18, AAV control TuD mice; n = 19, AAV–anti–mmu-miR-665-3p TuD mice). Statistical details are provided in Supplemental Table 13.