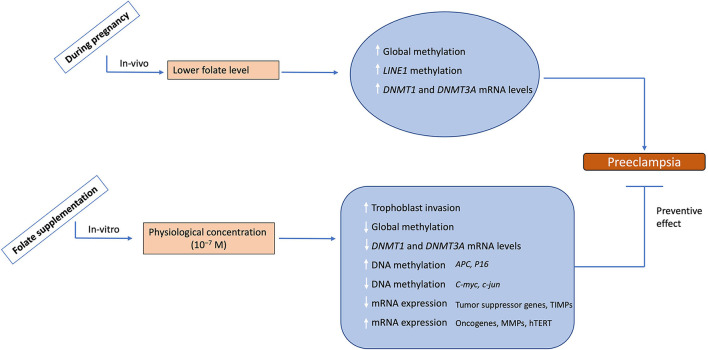
Figure 8.
Summary of the study. During physiological pregnancy lower levels to folate are associated with increased global methylation, LINE1 methylation and mRNA levels for DNMT1 and 3A leading to preeclampsia development. Folate supplementation at physiological levels leads to increased trophoblast invasion potential, decreased global methylation, decreased mRNA levels for DNMT1 and 3A, and alters DNA methylation/mRNA expression of various placental genes. This data demonestrates the possible role of folate supplementation in reversing the preeclampsia phenotype, hence suggesting a protective effect of folate supplementation. The upward arrows show an increase, while the downward arrows show the decrease in these parameters.