Figure 1. D2R upregulation does not alter intrinsic properties or firing in NAc CINs.
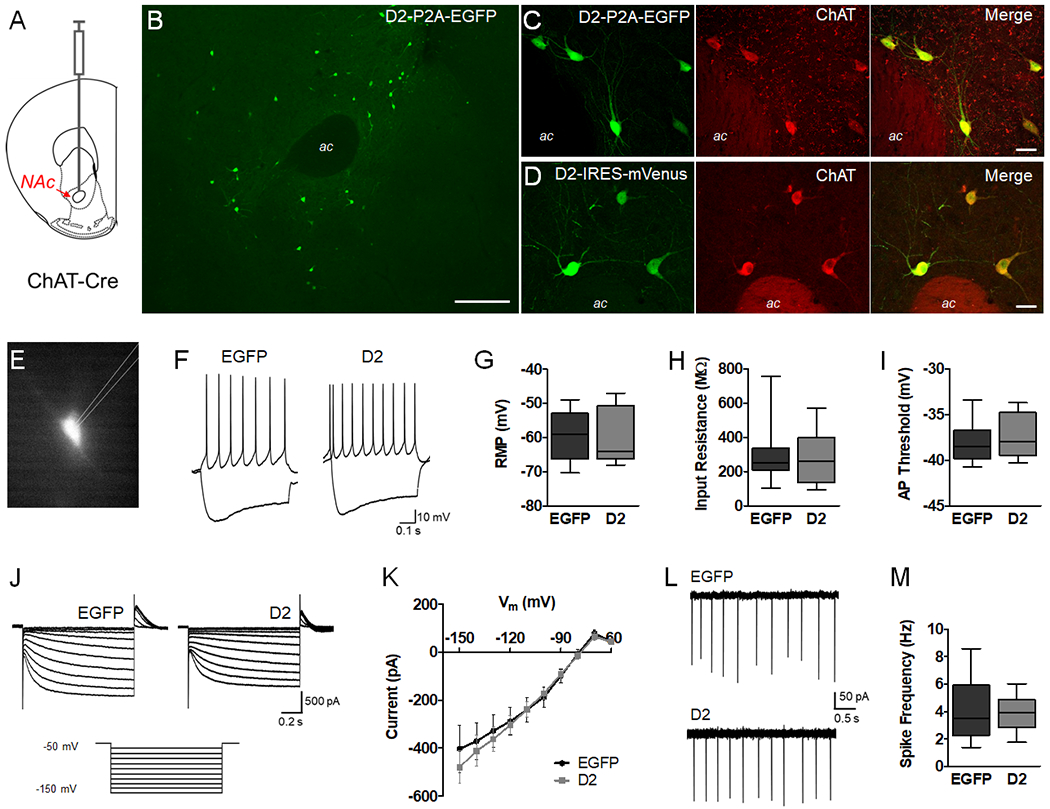
A. Schematic representation depicting injection of AAV into the NAc core of adult ChAT-Cre mice. B. Low magnification image of AAV-DIO-D2-P2A-EGFP expression in the NAc core 4 weeks after viral injection. Scale = 200 μm. C, D. Double-immunolabeling of AAV-DIO-D2-P2A-EGFP or AAV-DIO-D2-IRES-mVenus expression and the cholinergic cell marker ChAT. Scale = 20 μm. E. Representative epifluorescence image of ex vivo slice preparations from adult NAc, showing a visually identified EGFP-positive CIN. F. Current clamp recordings in whole-cell mode showing the voltage responses to −140 and +40 pA currents. G-I. Box plots (bars, min/max values; box, lower/upper quartile; line, median) showing resting membrane potential (t = 0.4814, p = 0.6341, n = 14-15 cells/group), input resistance (t = 0.3712, p = 0.7134, n = 14-15 cells/group) and action potential threshold (t = 0.7209, p = 0.4774, n = 14-15 cells/group) were not altered by D2R upregulation. Data was analyzed using unpaired t tests (two-tailed). J. Representative voltage clamp recordings showing currents induced by hyperpolarizing voltage steps from a holding potential of −50 mV (−60 to −150 mV). K. Ih was not altered by D2R upregulation (F(1,26) = 0.117, p = 0.7353, n = 14-15 cells/group). L, M. Cell-attached recordings to measure spontaneous CIN activity revealed no difference in spike frequency (t = 0.1134, p = 0.9108, n = 10-13 cells/group).
