FIGURE 6.
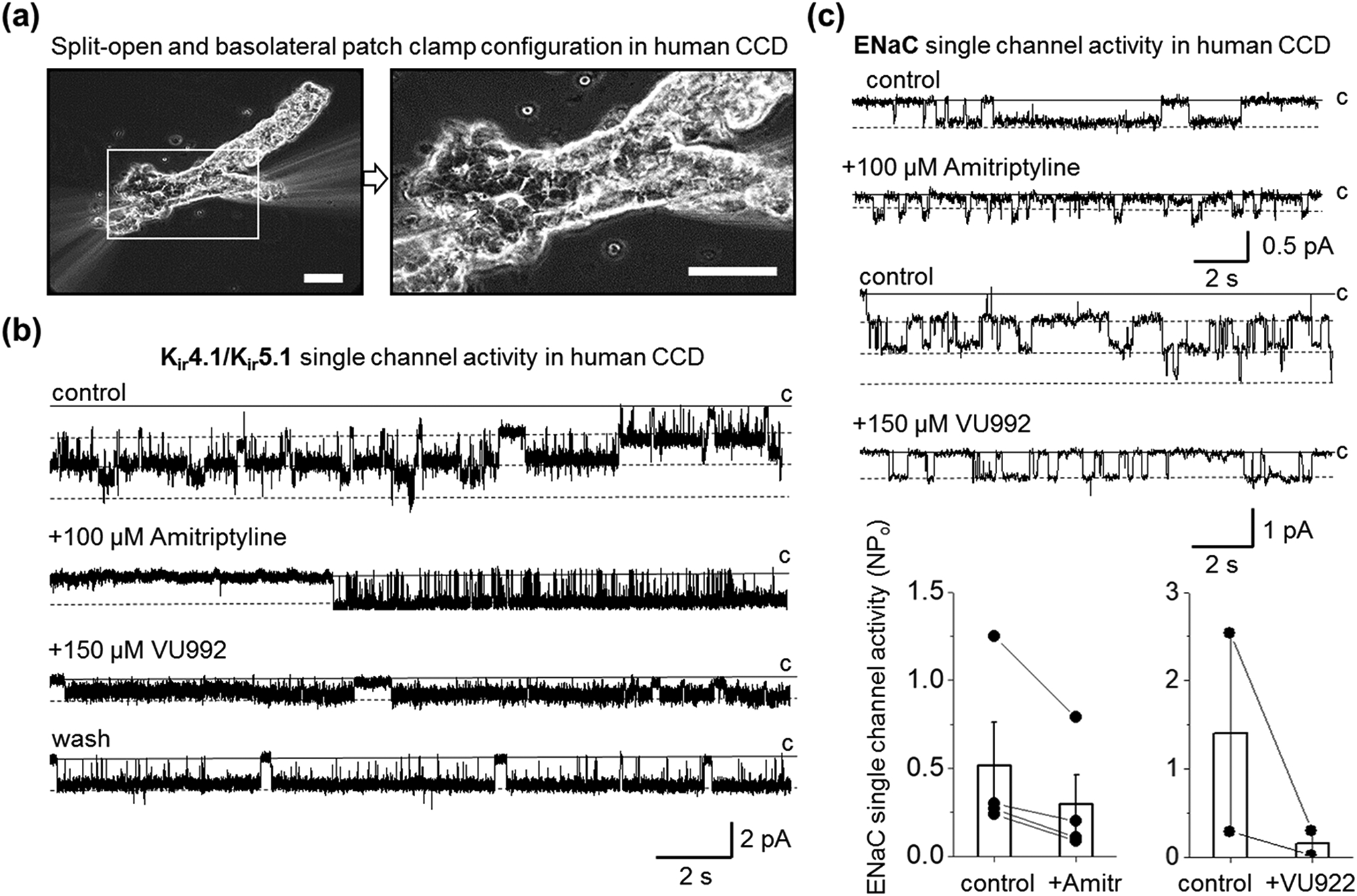
Inhibition of basolateral Kir4.1/Kir5.1 channel modulates ENaC activity in human CCD principal cells. (a) Representative image of patch-clamp configuration on apical (split-open) or basolateral parts of freshly isolated human CCD. Scale bars are 40 μm. (b) Representative current traces monitoring basolateral Kir4.1/Kir5.1 single-channel activity in cell-attached mode after application of PSS or DMSO as vehicle control or amitriptyline (100 μM) and subsequent addition of VU992 (150 μM). The patch was clamped to -Vp = −60 mV. The single-channel conductance of the recorded channel was 54 pS. Note that the effect of the application of VU992 was reversible (wash). (c) Representative current traces monitoring ENaC single-channel activity after application of PSS or DMSO as a vehicle control or amitriptyline (upper panel; -Vp = −40 mV) or VU992 (bottom; -Vp = −60 mV) applications. A solid line denotes a non-conducting closed state. Dash lines indicate open states. Summary graphs of changes in ENaC activity in response to amitriptyline (n = 4) and VU992 (n = 2) application are also shown.
