Extended Figure 1. Treg cell heterogeneity at homeostasis and Treg cell expression of PD-1.
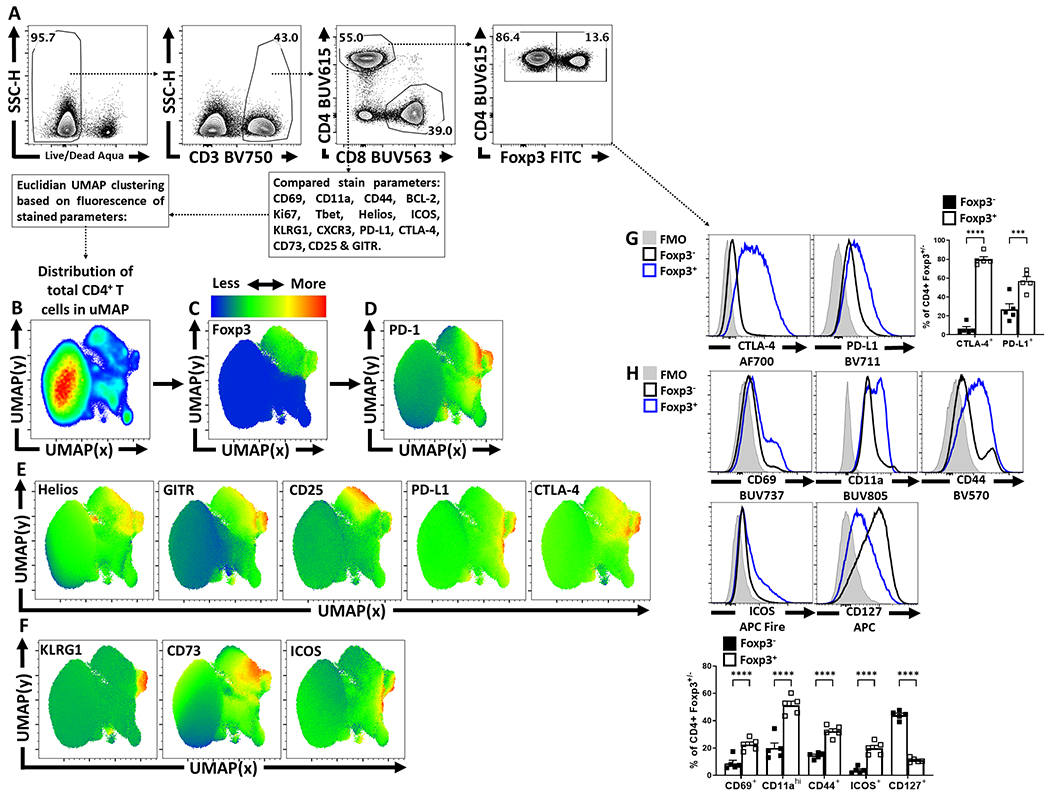
(A) Splenocytes from naïve 8 week-old male C57BL/6 mice were analyzed via high-parameter flow cytometry to identify CD4+ T cells, and subset them into Foxp3+ and Foxp3− subsets, depicted is the gating strategy to identify Treg and Tconv CD4+ T cells. (B) Qualitative analysis of bulk CD3+, CD4+ T cells was conducted to produce a 2-dimensional UMAP representation using dimensional reduction algorithms (excluding CD4, Foxp3, and PD-1 expression as calculated factors). (C-D) Regions of CD4+ T cells expressing Foxp3 and or PD-1 were identified via median heatmap of expression of the generated UMAP plot. (E) The initial distribution UMAP was then qualitatively assessed using median heatmap distribution trends amongst the bulk CD4+ T cell pool of Treg cell associated proteins: Helios, GITR, CD25, PD-L1, and CTLA-4, in addition to proteins associated with effector function in Tregs (F) KLRG1, CD73, and ICOS. (G) Histogram comparisons were then made and quantified between Foxp3+ and Foxp3− subsets for the inhibitory proteins CTLA-4 and PD-L1 (n = 5/group, 2 way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons test, *** = p = 0.0002, **** = p < 0.0001, 6 experimental replicates). (H) Proteins associated with activation (CD69, CD11a, CD44, ICOS, and CD127) were also compared and quantified (n = 5/group, 2 way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons test, **** = p < 0.0001, 6 experimental replicates). All data presented are means +/− SEM and show individual data points.
