Fig. 3. Analyses of Cdk1 in S-phase entry.
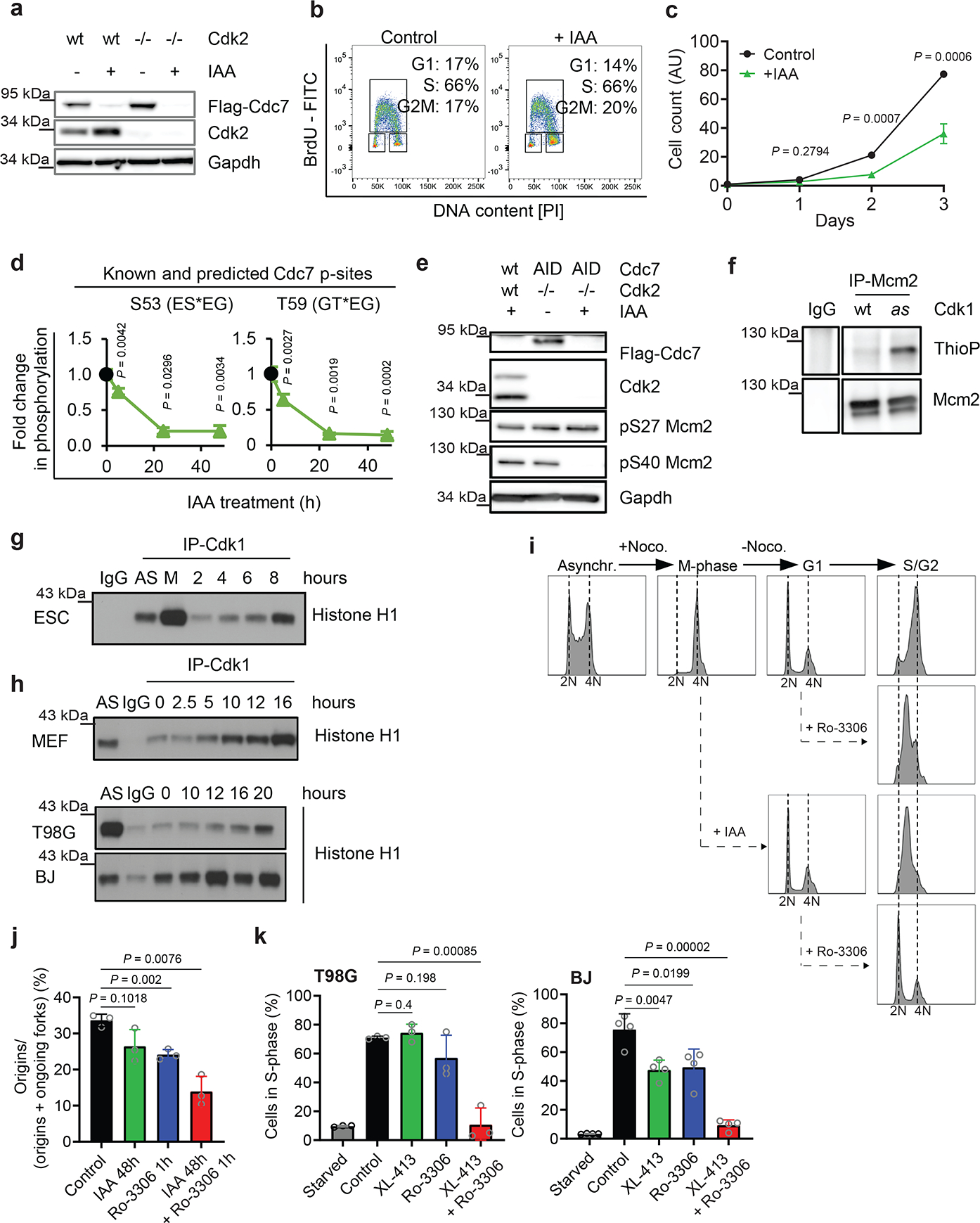
a, Immunoblotting of Cdk2+/+ (wt) and Cdk2-knockout (Cdk2−/−) Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC treated with auxin (IAA). b, Flow cytometry of Cdk2-knockout/Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC treated with auxin or vehicle (Control). c, Growth curves of Cdk2-knockout/Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC treated with auxin or vehicle. d, Quantification of Mcm2-phosphorylation in Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC treated with auxin for 5, 24, 48h. Black dots, phosphorylation levels at time 0. e, Immunoblotting of Cdk2+/+ (wt) and Cdk2−/−, Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 (AID) ESC for Cdc7-dependent (S40) and -independent (S27) Mcm2 phosphoresidues; cells were treated with auxin for 24h. f, In-cell phosphorylation of Mcm2 by Cdk1. IgG, control immunoprecipitation from Cdk1AS/AS cells. g, h, ESC were released from mitosis (g), MEFs, glioblastoma T98G and BJ foreskin fibroblasts were released from G0 (h). Cdk1 was immunoprecipitated at the indicated time-points and used for kinase reactions with histone H1 as substrate. AS, asynchronous cells; M, mitosis-arrested cells. IgG, control immunoprecipitation. i, Asynchronously growing Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC (Asynchr.) were synchronized in mitosis by nocodazole (M-phase) and released (−Noco). Upon release, Cdc7 degradation was induced by auxin addition to account for degradation time. Two hours later, when cells reached G1, they were treated with Cdk1 inhibitor Ro-3306. Cells were cultured in the presence of inhibitor(s), collected after 12h (S/G2), stained with propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry. j, Fraction of new replication origins in Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC treated with auxin for 48 h and/or Ro-3306 for the last 1h, or with vehicle. k, T98G and BJ cells were arrested in G0 and released in the presence of CDC7 inhibitor XL-413 and/or Ro-3306 or vehicle. Cells were pulsed with BrdU after 19h and analyzed by flow cytometry. c, d, j,k, mean values; p-values two-sided t-test; error bars, SD. c, d, j, k, n=3 independent replicates; a, b, e-i representative results (out of 2).
