Extended Data Fig. 2. Analyses of Cdc7AID/AID cells.
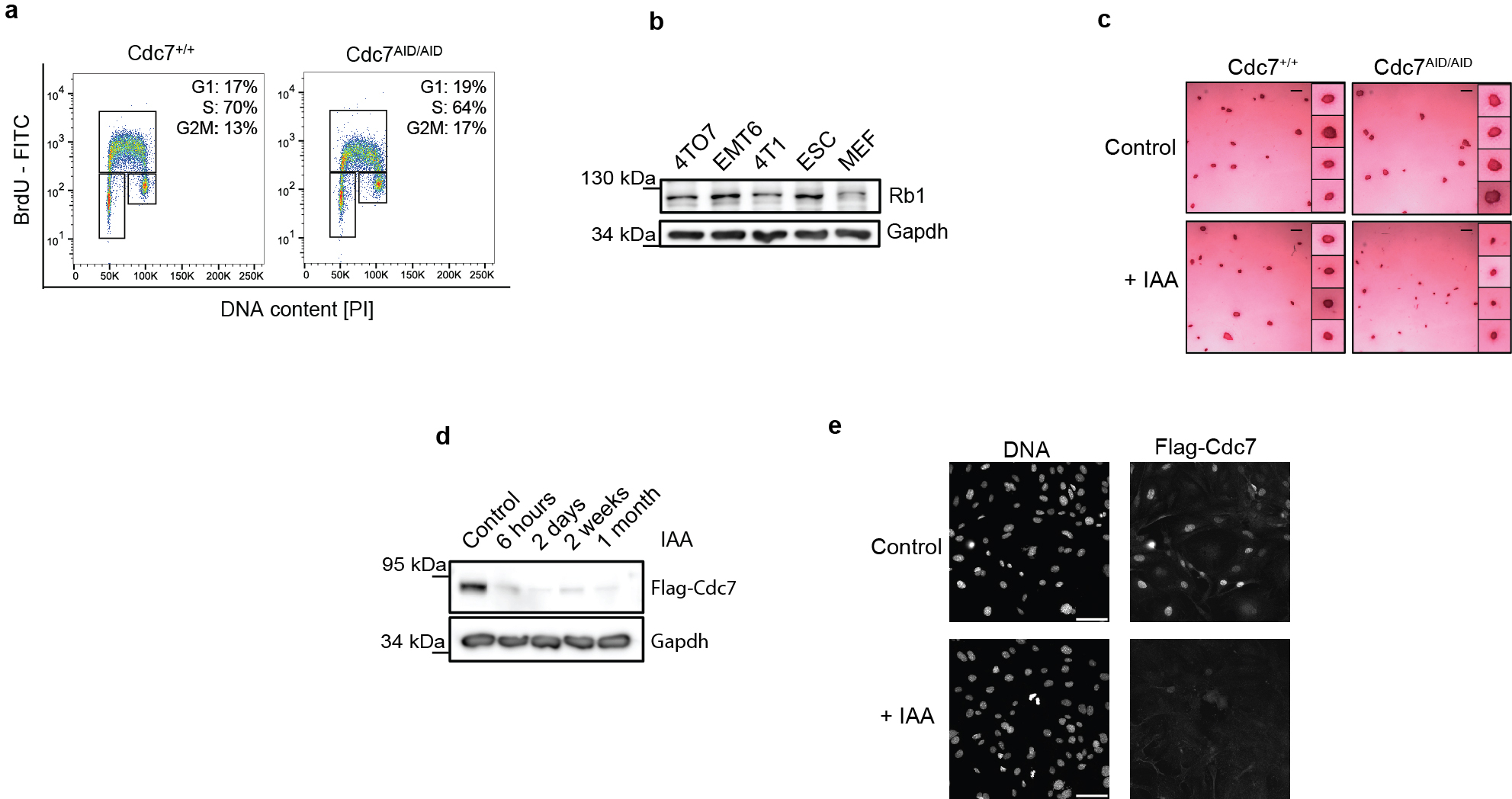
a, wild-type (Cdc7+/+) and Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC were cultured without auxin. Cells were pulsed with BrdU, stained with an anti-BrdU antibody and propidium iodide and analyzed by flow cytometry. Note normal cell cycle profile of Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC in the absence of auxin, as expected. b, Immunoblot analysis to demonstrate expression of the retinoblastoma protein, Rb1, in wild-type ESC. Whole cell lysates from MEFs and mouse breast cancer cell lines (4TD8, EMT6, 4T1) were immunoblotted for control. c, Cdc7+/+ and Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC were cultured on feeders with auxin (IAA) or vehicle (Control) for 72 h and stained for alkaline phosphatase, a marker of undifferentiated pluripotent stem cells. Scale bar, 500 μm. Inserts, higher magnification of colonies. Inhibition of Cdc7 did not decrease alkaline phosphatase staining, suggesting that Cdc7 is not required to maintain pluripotency. d, Cdc7 protein levels in Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 ESC cultured with auxin for the indicated times. Immunoblots of whole cell lysates were probed with an anti-Flag antibody to detect Flag-tagged endogenous Cdc7. Efficient degradation of Cdc7 was maintained after 1 month of continuous culture with auxin. e, Immunostaining of Cdc7AID/AID/Tir1 MEFs for expression of Cdc7. Cells were cultured with vehicle or auxin for 4 h, and stained with an anti-Flag antibody. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst. Note the loss Cdc7 staining after addition of auxin. See Fig. 1k for quantification. a-e, representative results (out of 2).
